Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 707-714.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.05.005
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yajieshaba prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal barrier injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis
YANG Liping, YU Xinglin, ZHANG Chao, CHEN Pu, DUAN Xiaohua( )
)
- Yunnan Key Laboratory of Dai and Yi Medicines, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, China
-
Received:2021-05-22Accepted:2021-08-23Online:2022-09-02Published:2022-09-02 -
Contact:DUAN Xiaohua -
About author:DUAN Xiaohua, Yunnan Key Laboratory of Dai and Yi Medicines, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, China. duanxiaohua@ynutcm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-871-65919481
-
Supported by:Grant from the Scientific Research Project of Yunnan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Protective Effect and Mechanism of Yajie Prescription on Intestinal Mucosal Barrier(2015DYYJ101);Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department-Applied Basic Research Joint Special Funds of Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Study on the Protective Effect and Mechanism of the Dai Medicine "Yajieshaba" on Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Food Allergic Mice(2017FF116-026)
Cite this article
YANG Liping, YU Xinglin, ZHANG Chao, CHEN Pu, DUAN Xiaohua. Yajieshaba prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal barrier injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 707-714.
share this article
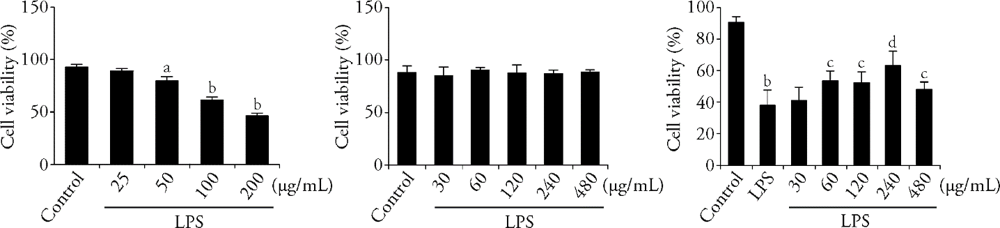
Figure 1YJSB attenuates LPS-mediated IEC-6 cell cytotoxicity A: IEC-6 cells were treated with LPS at various concentrations (25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL) for 24 h; B: IEC-6 cells were incubated with YJSB (30, 60, 120, 240, 480 μg/mL) for 24 h. C: IEC-6 cells were treated with YJSB (30, 60, 120, 240, 480 μg/mL) and LPS (l00 μg/mL) for 24 h. YJSB: Yajieshaba; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01vs control group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs LPS group.

Figure 2 Effect of YJSB on the expression of TJ proteins A: the TJ integrity of IEC-6 cells was observed by fluorescence microscope using Hoechst staining, suggested that LPS altered the distribution of TJ protein at cell boundaries, and this effect was significantly inhibited by YJSB (×200 magnification), A1, B1, C1: control groups; A2, B2, C2: LPS groups; A3, B3, C3: YJSB groups; B: Western blot detection of the expression of TJ proteins in mice intestines. TJ: tight junction; YJSB: Yajieshaba; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; ZO-1: zonulaoccludens-1. aP < 0.01 vs control group; bP < 0.05 vs LPS group.

Figure 3 Effect of YJSB on intestinal histological appearance and permeability A: D-Lactate; B: DAO; C: effect of YJSB on body weight of the mice; D: intestinal histopathological injury was observed by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining (×100), D1: control group; D2,: LPS group; D3, D4: YJSB groups; E: villus heights; F: crypt depth. G: V/C. YJSB: Yajieshaba; LPS: lipopolysaccharide. V/C: villus height /crypt depth ratio; DAO: diamine oxidase. aP < 0.01 vs control group; bP < 0.05 vs LPS group.

Figure 4 Effect of YJSB on LPS-induced apoptosis Western blot detection of the expression levels of Bcl-2 and Bax in mice intestines. A: Bcl-2 and Bax protein levels were determined by Western bloting; B: relative density of Bcl-2 and Bax. YJSB: Yajieshaba; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax: Bcl-2 assaciated X protein. aP < 0.01vs control group; bP < 0.01 vs LPS group.
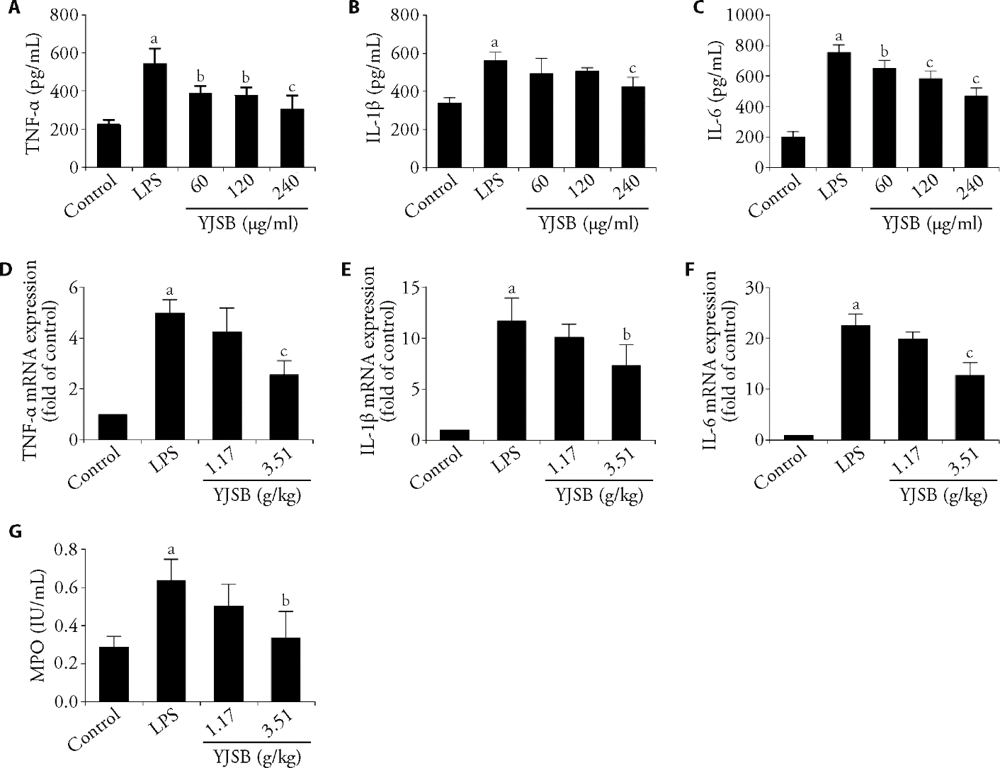
Figure 5 YJSB ameliorates LPS-induced inflammatory response TNF-α (A), IL-1β (B) and IL-6 (C) in IEC-6 cells. mRNA levels of TNF-α (D), IL-1β (E) and IL-6 (F) in jejunum homogenates of mice. MPO level in mice plasma (F). YJSB: Yajieshaba; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-6: interleukin-6; MPO: myeloperoxidase; aP < 0.01 vs vehicle control group. bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01vs LPS-treated group.

Figure 6 Mechanism of YJSB in protecting the intestinal barrier function YJSB: Yajieshaba; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; ZO-1: zonulaoccludens-1; DAO: diamine oxidase; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax: Bcl-2 assaciated X protein; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-6: interleukin-6; MPO: myeloperoxidase.
| 1. |
Farhadi A, Banan A, Fields J, Keshavarzian A. Intestinal barrier: an interface between health and disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003; 18: 479-97.
DOI URL |
| 2. |
Martini E, Krug SM, Siegmund B, Neurath MF, Becker C. Mend your fences: the epithelial barrier and its relationship With Mucosal Immunity in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 4: 33-46.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Konig J, Wells J, Cani PD, et al. Human intestinal barrier function in health and disease. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2016; 7: e196.
DOI URL |
| 4. |
Mankertz J, Schulzke JD. Altered permeability in inflammatory bowel disease: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2007; 23: 379-83.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Blikslager AT, Moeser AJ, Gookin JL, Jones SL, Odle J. Restoration of barrier function in injured intestinal mucosa. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 545-64.
PMID |
| 6. | Chelakkot C, Ghim J, Ryu SH. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp Mol Med 2018; 50: 103. |
| 7. | Williams JM, Duckworth CA, Watson AJ, et al. A mouse model of pathological small intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and shedding induced by systemic administration of lipopolysaccharide. Dis Model Mech 2013; 6: 1388-99. |
| 8. |
Song D, Zong X, Zhang H, et al. Antimicrobial peptide Cathelicidin-BF prevents intestinal barrier dysfunction in a mouse model of endotoxemia. Int Immunopharmacol 2015; 25: 141-7.
DOI URL |
| 9. |
Deitch EA, Ma L, Ma WJ, et al. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced bacterial translocation in mice. J Clin Invest 1989; 84: 36-42.
PMID |
| 10. |
Caradonna L, Amati L, Magrone T, Pellegrino NM, Jirillo E, Caccavo D. Enteric bacteria, lipopolysaccharides and related cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease: biological and clinical significance. J Endotoxin Res 2000; 6: 205-14.
PMID |
| 11. |
Han X, Fink MP, Yang R, Delude RL. Increased iNOS activity is essential for intestinal epithelial tight junction dysfunction in endotoxemic mice. Shock 2004; 21: 261-70.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Guo S, Al-Sadi R, Said HM, Ma TY. Lipopolysaccharide causes an increase in intestinal tight junction permeability in vitro and in vivo by inducing enterocyte membrane expression and localization of TLR-4 and CD14. Am J Pathol 2013; 182: 375-87.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Nighot M, Al-Sadi R, Guo S, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight permeability is mediated by toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) activation of myosin light chain kinase expression. Am J Pathol 2017; 187: 2698-2710.
DOI URL |
| 14. | Jia KL, Zhao YH. Dai medical pharmacology. Beijing: Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Chu Ban She, 2007: 161-162. |
| 15. | Lin YF, Qiu MF, Jia W, Dao Hi, Wang YJ. Overview of Chinese Dai medical research (Review). Zhong Guo Min Zu Yi Yao Za Zhi 2007: 1-5. |
| 16. | Zhang C. Basic theory of Dai medicine. Beijing: Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Chu Ban She, 2007: 57-59. |
| 17. | Li QC. Mechanism of Dai Formula Yajieshaba detoxifying food poison for food allergy treatment. Beijing: University of Chinese Medicine, 2017: 135. |
| 18. |
Zhang GY, Duan XH, Zhang C, Chen P, Yu J, Zheng J. Immunoregulatory effects of the traditional Dai prescription Yajieshaba on food allergic mice. Exp Ther Med 2017; 13: 3175-3182.
DOI URL |
| 19. |
Han F, Lu Z, Liu Y, et al. Cathelicidin-BF ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal epithelial barrier disruption in rat. Life Sci 2016; 152: 199-209.
DOI URL |
| 20. |
Sun XQ, Fu XB, Zhang R, et al. Relationship between plasma D(-)-lactate and intestinal damage after severe injuries in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7: 555-8.
DOI URL |
| 21. |
Jin X, Yu CH, Lv GC, Li YM. Increased intestinal permeability in pathogenesis and progress of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13: 1732-6.
DOI URL |
| 22. |
Matsumoto Y, Nakanishi Y, Yoshioka T, et al. Epithelial EP4 plays an essential role in maintaining homeostasis in colon. Sci Rep 2019; 9: 15244.
DOI URL |
| 23. | Hsieh CY, Osaka T, Moriyama E, Date Y, Kikuchi J, Tsuneda S. Strengthening of the intestinal epithelial tight junction by Bifidobacterium bifidum. Physiol Rep 2015; 3. |
| 24. | Wu QJ, Wang YQ, Qi YX. The protective effect of procyanidin against LPS-induced acute gut injury by the regulations of oxidative state. Springer Plus 2016; 5: 1645. |
| 25. |
Travis S, Menzies I. Intestinal permeability: functional assessment and significance. Clin Sci 1992; 82: 471-88.
PMID |
| 26. |
Nusrat A, Turner JR, Madara JL. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions. IV. Regulation of tight jun-ctions by extracellular stimuli: nutrients, cytokines, and immune cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000; 279: G851-7.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Wang T, Yao W, Li J, et al. Dietary garcinol supplementation improves diarrhea and intestinal barrier function associated with its modulation of gut microbiota in weaned piglets. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 2020; 11: 12.
DOI URL |
| 28. | Araki Y, Mukaisyo K, Sugihara H, Fujiyama Y, Hattori T. Increased apoptosis and decreased proliferation of colonic epithelium in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Oncol Rep 2010; 24: 869-74. |
| 29. |
Chin AC, Teoh DA, Scott KG, Meddings JB, Macnaughton WK, Buret AG. Strain-dependent induction of enterocyte apoptosis by Giardia lamblia disrupts epithelial barrier function in a caspase-3-dependent manner. Infect Immun 2002; 70: 3673-80.
DOI URL |
| 30. | Nan X, Qin S, Yuan Z, et al. Hsa-miRNA-31 regulates epithelial cell barrier function by inhibiting TNFSF15 expression. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2016; 62: 104-10. |
| 31. | Novak EA, Mollen KP. Mitochondrial dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 2015; 3: 62. |
| 32. |
Chen J, Zhang R, Wang J, et al. Protective effects of baicalin on LPS-induced injury in intestinal epithelial cells and intercellular tight junctions. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2015; 93: 233-7.
DOI URL |
| 33. | Sadar SS, Vyawahare NS, Bodhankar SL. Ferulic acid ameliorates TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis through modulation of cytokines, oxidative stress, iNOs, COX-2, and apoptosis in laboratory rats. Excli J 2016; 15: 482-499. |
| 34. |
Moldoveanu AC, Diculescu M, Braticevici CF. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Rom J Intern Med 2015; 53: 118-27.
PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

