Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 329-336.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20221226.003
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of acupuncture on repair of glial scars in rats with traumatic brain injury
ZENG Hai1, CAO Luxi1, PANG Zhao2, ZHAO Sisi1, WANG Shiqi1, LIN Zhuowen1, CHEN Minan1, LIN Shujun3( ), ZHANG Yimin1(
), ZHANG Yimin1( )
)
- 1 Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Medical Administration Division, the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, China
3 Medical College of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Rehabilitation, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
-
Received:2021-11-22Accepted:2022-04-04Online:2023-04-15Published:2023-03-14 -
Contact:ZHANG Yimin, Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China. zhangymjnu@163.com; LIN Shujun, Medical College of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Rehabilitation, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China. 050099@gzucm.edu.cn. Telephone: +86-20-85228016 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Explore the Effect and Mechanism of Acupuncture for Neuroinflammation and Glial Scars After Traumatic Brain Injury Based on the Signaling Pathway of TLR2/4-NFκB(81574066);National Natural Science Foundation of China: Explore the Effect of Acupuncture on Brain Function Remodeling and the Benign Bidirectional Regulation to Autophagy After TBI(81873362);National Natural Science Foundation of China: Basing on the Theory of Bidirectional Benign Regulation to Investigate the Mechanism of Acupuncture Regulating Microglia-mediated Immune Imbalance to Promote Nerve Repair After TBI(82174483);National Natural Science Foundation of China: Based on Iron Metabolic Pathway to Explore the Mechanism of Electroacupuncture Inhibits Ferroptosis to Reduce TBI Nerve Injury(82205249);China Postdoctoral Science Foundation: the Effect and Mechanism of Electroacupuncture in Promoting Neural Function Repair by Regulating Iron Metabolism in Neurons of TBI Rats(2022M710912);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province: the Effect and Mechanism of Acupuncture on the Linkage of Neuron Autophagy and Apoptosis after TBI Based on PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway(2021A1515011219);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province: the Effect and Mechanism of Acupuncture on Microglial Polarization Mediated Immune Homeostasis After TBI Based on TREM2/STAT6/NFκB Signaling Pathway(2021A1515110146)
Cite this article
ZENG Hai, CAO Luxi, PANG Zhao, ZHAO Sisi, WANG Shiqi, LIN Zhuowen, CHEN Minan, LIN Shujun, ZHANG Yimin. Efficacy of acupuncture on repair of glial scars in rats with traumatic brain injury[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 329-336.
share this article
| Group | 1st day | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 18.0±0.0 | 18.0±0.0 | 18.0±0.0 | 18.0±0.0 | 18.0±0.0 |
| Model | 5.8±0.8a | 7.4±0.8a | 8.0±1.0a | 10.2±0.9a | 16.0±1.3a |
| Acupuncture | 5.8±0.6b | 9.5±0.5b | 12.7±0.6b | 14.8±0.9b | 17.6±0.5b |
Table 1 Change in neurobehavioral scores in three groups ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | 1st day | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 18.0±0.0 | 18.0±0.0 | 18.0±0.0 | 18.0±0.0 | 18.0±0.0 |
| Model | 5.8±0.8a | 7.4±0.8a | 8.0±1.0a | 10.2±0.9a | 16.0±1.3a |
| Acupuncture | 5.8±0.6b | 9.5±0.5b | 12.7±0.6b | 14.8±0.9b | 17.6±0.5b |

Figure 1 Effect of acupuncture on the morphology of the perilesional cortex A-L: hematoxylin-eosin staining in three groups (×100 magnification). A-D: the morphology of the cortex in the normal group on days 3, 7, 14, and 28. E-H: the morphology of the perilesional cortex in the model group on days 3, 7, 14, and 28. I-L: the morphology of the perilesional cortex in the acupuncture group on days 3, 7, 14, and 28. Normal group: rats without TBI modeling and acupuncture treatment; model group: rats with TBI modeling; acupuncture group: rats with TBI modeling and acupuncture treatment. TBI: traumatic brain injury.
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 9.7±3.1 | 11.0±1.0 | 10.7±3.2 | 11.3±1.5 |
| Model | 17.7±3.0a | 32.3±7.4a | 25.0±4.0a | 23.0±3.4a |
| Acupuncture | 31.3±5.9b | 24.4±3.8b | 22.0±3.6b | 16.0±3.6b |
Table 2 Effect of acupuncture on the number of astrocytes ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 9.7±3.1 | 11.0±1.0 | 10.7±3.2 | 11.3±1.5 |
| Model | 17.7±3.0a | 32.3±7.4a | 25.0±4.0a | 23.0±3.4a |
| Acupuncture | 31.3±5.9b | 24.4±3.8b | 22.0±3.6b | 16.0±3.6b |
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 2.0±1.7 | 2.7±2.1 | 2.3±0.6 | 1.9±1.0 |
| Model | 14.3±1.2a | 33.3±5.1a | 27.0±4.6a | 28.3±2.5a |
| Acupuncture | 18.3±2.5b | 28.8±5.9b | 18.3±3.1b | 12.7±2.5b |
Table 3 Effect of acupuncture on the number of microglia ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 2.0±1.7 | 2.7±2.1 | 2.3±0.6 | 1.9±1.0 |
| Model | 14.3±1.2a | 33.3±5.1a | 27.0±4.6a | 28.3±2.5a |
| Acupuncture | 18.3±2.5b | 28.8±5.9b | 18.3±3.1b | 12.7±2.5b |
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 29.0±3.0 | 27.3±4.7 | 28.0±4.6 | 29.7±1.5 |
| Model | 9.3±0.6a | 13.3±4.9a | 12.0±3.6a | 16.7±3.5a |
| Acupuncture | 15.0±2.0b | 19.3±1.5b | 22.7±3.5b | 24.7±1.5b |
Table 4 Effect of acupuncture on the number of neurons ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 29.0±3.0 | 27.3±4.7 | 28.0±4.6 | 29.7±1.5 |
| Model | 9.3±0.6a | 13.3±4.9a | 12.0±3.6a | 16.7±3.5a |
| Acupuncture | 15.0±2.0b | 19.3±1.5b | 22.7±3.5b | 24.7±1.5b |
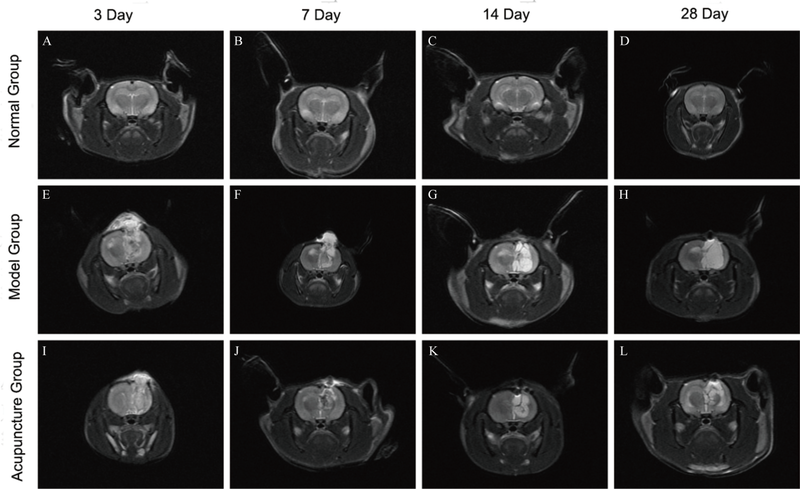
Figure 2 Representative coronal T2-weighted images of three groups A-D: the coronal T2-weighted images of the brain in the normal group on days 3, 7, 14, and 28. E-H: the coronal T2-weighted images of the brain in the model group on days 3, 7, 14, and 28. I-L: the coronal T2-weighted images of the brain in the acupuncture group on days 3, 7, 14, and 28. Normal group: rats without TBI modeling and acupuncture treatment; model group: rats with TBI modeling; acupuncture group: rats with TBI modeling and acupuncture treatment. TBI: traumatic brain injury.
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 282±33 | 274±42 | 302±48 | 319±42 |
| Acupuncture | 287±74 | 247±35a | 255±41a | 253±27a |
Table 5 Effect of acupuncture on the lesion volume (mm3, $\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 282±33 | 274±42 | 302±48 | 319±42 |
| Acupuncture | 287±74 | 247±35a | 255±41a | 253±27a |
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 0.257±0.046 | 0.257±0.028 | 0.258±0.040 | 0.256±0.041 |
| Model | 0.145±0.010a | 0.160±0.007a | 0.133±0.012a | 0.148±0.023a |
| Acupuncture | 0.149±0.006b | 0.176±0.007b | 0.179±0.014b | 0.212±0.020b |
Table 6 Effect of acupuncture on the FA value ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | 3rd day | 7th day | 14th day | 28th day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 0.257±0.046 | 0.257±0.028 | 0.258±0.040 | 0.256±0.041 |
| Model | 0.145±0.010a | 0.160±0.007a | 0.133±0.012a | 0.148±0.023a |
| Acupuncture | 0.149±0.006b | 0.176±0.007b | 0.179±0.014b | 0.212±0.020b |
| 1. | Reis C, Gospodarev V, Reis H, et al. Traumatic brain injury and stem cell: pathophysiology and update on recent treatment modalities. Stem Cells Int 2017; 2017: 6392592. |
| 2. |
GBD 2016 Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol 2019; 18: 56-87.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Chiu CC, Liao YE, Yang LY, et al. Neuroinflammation in animal models of traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Methods 2016; 272: 38-49.
DOI URL |
| 4. |
Liddelow SA, Guttenplan KA, Clarke LE, et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017; 541: 481-7.
DOI |
| 5. |
Perez JC, Gerber YN, Perrin FE. Dynamic diversity of glial response among species in spinal cord injury. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13: 769548.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Zhou Y, Shao A, Yao Y, Tu S, Deng Y, Zhang J. Dual roles of astrocytes in plasticity and reconstruction after traumatic brain injury. Cell Commun Signal 2020; 18: 62.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Jiang S, Chen W, Zhang Y, et al. Acupuncture induces the proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells in rats with traumatic brain injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016; 2016: 2047412. |
| 8. | Bao Z, Fang K, Miao Z, et al. Human cerebral organoid implantation alleviated the neurological deficits of traumatic brain injury in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021; 2021: 6338722. |
| 9. |
Anderson MA, Burda JE, Ren Y, et al. Astrocyte scar formation aids central nervous system axon regeneration. Nature 2016; 532: 195-200.
DOI |
| 10. | Tan L, Zeng L, Wang N, et al. Acupuncture to promote recovery of disorder of consciousness after traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 5190515. |
| 11. | Guo ZQ, Huang Y, Jiang H, Wang WB. Randomized clinical trials of early acupuncture treatment of limb paralysis in traumatic brain injury patients and its mechanism. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2019; 44: 589-93. |
| 12. |
Juan YH, Livneh H, Huang HJ, Lu MC, Yeh CC, Tsai TY. Decreased risk of dementia among patients with traumatic brain injury receiving acupuncture treatment: a population-based retrospective cohort study. J Head Trauma Rehabil 2019; 34: e17-23.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Lin SJ, Cao LX, Cheng SB, et al. Effect of acupuncture on the TLR2/4-NF-κB signalling pathway in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Acupunct Med 2018; 36: 247-53.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Ye L, Yang Y, Zhang X, et al. The role of bFGF in the excessive activation of astrocytes is related to the Inhibition of TLR4/NFκB Signals. Int J Mol Sci 2015; 17: 37.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Karova K, Wainwright JV, Machova-Urdzikova L, et al. Transplantation of neural precursors generated from spinal progenitor cells reduces inflammation in spinal cord injury via NF-κB pathway inhibition. J Neuroinflammation 2019; 16: 12.
DOI |
| 16 |
Yuan J, Liu W, Zhu H, et al. Curcumin inhibits glial scar formation by suppressing astrocyte-induced inflammation and fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res 2017; 1655: 90-103.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Wang S, Lin S, Zhu M, et al. Acupuncture reduces apoptosis of granulosa cells in rats with premature ovarian failure via restoring the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 6311.
DOI URL |
| 18. |
Vázquez-Rosa E, Shin MK, Dhar M, et al. P7C3-A 20 treatment one year after TBI in mice repairs the blood-brain barrier, arrests chronic neurodegeneration, and restores cognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2020; 117: 27667-75.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Zhu MM, Lin JH, Qing P, et al. Manual acupuncture relieves microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in a rat model of traumatic brain injury by inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK2 pathway. Acupunct Med 2020; 38: 426-34.
DOI URL |
| 20. | Chen FF, Song WT, Guo SY, et al. Comparison of three kinds of neurological function rating systems on focal cerebral ischemia models of rodent animals. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2011; 26: 337-41. |
| 21. | Liu Y, Wang R. Role of reactive astrocytes after traumatic brain injury. Jing Shen Ji Bing Yu Jing Shen Wei Sheng 2017; 17: 747-50. |
| 22. |
Donat CK, Scott G, Gentleman SM, Sastre M. Microglial activation in traumatic brain injury. Front Aging Neurosci 2017; 9: 208.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Colonna M, Butovsky O. Microglia function in the central nervous system during health and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol 2017; 35: 441-68.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Fumagalli M, Lombardi M, Gressens P, Verderio C. How to reprogram microglia toward beneficial functions. Glia 2018; 66: 2531-49.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Yang YH, Zhu J. Targeting miR-106-3p facilitates functional recovery via inactivating inflammatory microglia and interfering glial scar component deposition after neural injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019; 23: 9000-8. |
| 26. |
Loane DJ, Kumar A. Microglia in the TBI brain: The good, the bad, and the dysregulated. Exp Neurol 2016; 275 Pt 3: 316-27.
DOI URL |
| 27. | Gong HX, Liu CH, Jia FQ, Wu Y. The research progress of GFAP and VEGF expression in traumatic brain injury. Zhong Guo Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016; 31: 144-7. |
| 28. | Yu GJ. Effects of VEGI on the activation and polarization of microglia in traumatic brain injury mice. Tianjin: Tianjin Medical University, 2016: 13-39. |
| 29. | Guo SS, Wang EP, Sun HL. Application of diffusion tensor imaging in the diagnosis of central nervous system diseases. Zhong Guo Shi Yong Shen Jing Ji Bing Za Zhi 2017; 20: 55-7. |
| 30. |
Soni N, Mohamed AZ, Kurniawan ND, Borges K, Nasrallah F. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging unveils the spatiotemporal microstructural gray matter changes following Injury in the rodent brain. J Neurotrauma 2019; 36: 1306-17.
DOI URL |
| 31. |
Villapol S, Byrnes KR, Symes AJ. Temporal dynamics of cerebral blood flow, cortical damage, apoptosis, astrocyte-vasculature interaction and astrogliosis in the pericontusional region after traumatic brain injury. Front Neurol 2014; 5: 82.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Tsao CC, Baumann J, Huang SF, et al. Pericyte hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) drives blood-brain barrier disruption and impacts acute ischemic stroke outcome. Angiogenesis 2021; 24: 823-42.
DOI |
| 33. |
Wu YG, Chao Y, Gao G, et al. Risk factors for cerebral infarction after moderate or severe traumatic brain injury. Ther Clin Risk Manag 2021; 17: 433-40.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Sandsmark DK, Bashir A, Wellington CL, Diaz-Arrastia R. Cerebral microvascular injury: a potentially treatable endophenotype of traumatic brain injury-induced neurodegeneration. Neuron 2019; 103: 367-79.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Obenaus A, Ng M, Orantes AM, et al. Traumatic brain injury results in acute rarefication of the vascular network. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 239.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Kenney K, Amyot F, Haber M, et al. Cerebral vascular injury in traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 2016; 275 Pt 3: 353-66.
DOI URL |
| 37. |
Griffin AD, Turtzo LC, Parikh GY, et al. Traumatic microbleeds suggest vascular injury and predict disability in traumatic brain injury. Brain 2019; 142: 3550-64.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Logsdon AF, Lucke-Wold BP, Turner RC, Huber JD, Rosen CL, Simpkins JW. Role of microvascular disruption in brain damage from traumatic train injury. Compr Physiol 2015; 5: 1147-60.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

