Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 633-6400.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220607.001
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Factors influencing physician's behavioral intention to use Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat coronavirus disease 2019 based on the theory of planned behavior
CHEN Huang1,2, SHI Lushaobo2,3, SHI Zengping2,3, XIA Yi2,3( ), WANG Dong2,3(
), WANG Dong2,3( )
)
- 1 General Office, the People’s Government of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510045, China
2 the Public Health Service System Construction Research Foundation of Guangzhou, Guangzhou 510515, China
3 School of Health Management, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China
-
Received:2022-02-22Accepted:2022-05-30Online:2022-08-15Published:2022-07-12 -
Contact:XIA Yi,WANG Dong -
About author:WANG Dong, School of Health Management, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China; the Public Health Service System Construction Research Foundation of Guangzhou, Guangzhou 510515, China. dongw96@smu.edu.cn, Telephone: +86-20-61647576
XIA Yi, School of Health Management, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China; the Public Health Service System Construction Research Foundation of Guangzhou, Guangzhou 510515, China. xiayi89@126.com;
-
Supported by:Research on the Management Mechanism of Integrating Traditional and Western Medicine to Responsed to Major Epidemic(20VYJ069)
Cite this article
CHEN Huang, SHI Lushaobo, SHI Zengping, XIA Yi, WANG Dong. Factors influencing physician's behavioral intention to use Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat coronavirus disease 2019 based on the theory of planned behavior[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 633-6400.
share this article
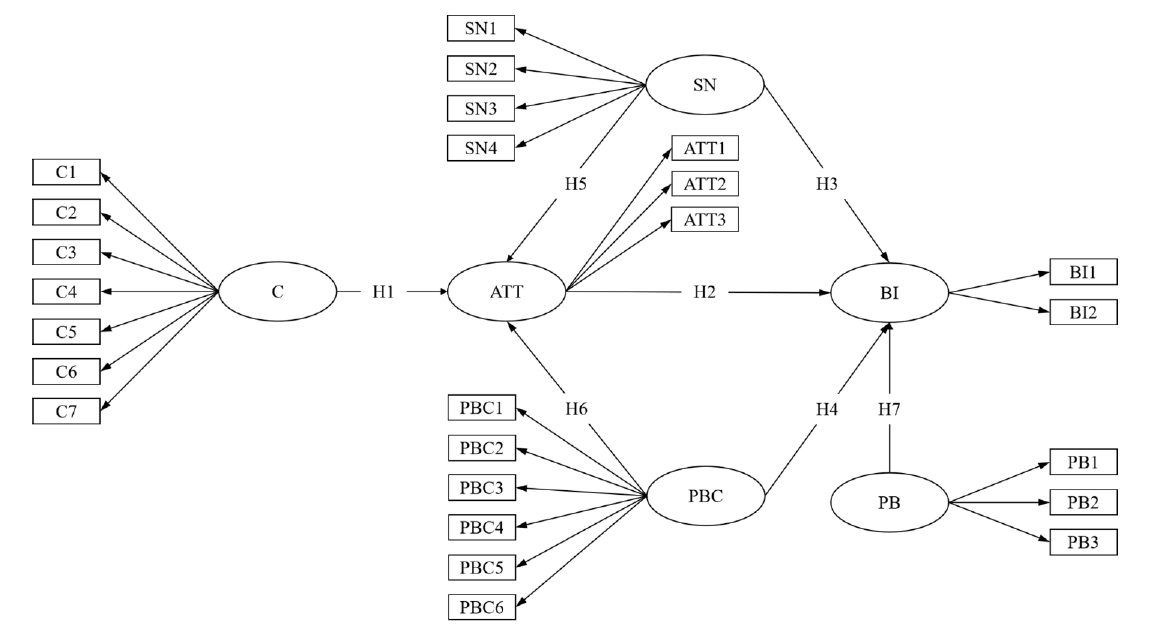
Figure 1 Constructs of conceptual model C: cognition; ATT: attitude; SN: subjective norms; PBC: perceived behavioral control; PB: past behavior; BI: behavior intention. H1: C positively affects physicians’ attitudes toward Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). H2: Attitude positively affects physicians’ intention to use TCM. H3: SN positively affects physicians’ intention to use TCM. H4: PBC positively affects physicians’ intention to use TCM. H5: SN positively affects physicians’ attitudes toward TCM. H6: PBC positively affects physicians’ attitudes toward TCM. H7: PB positively affects physicians’ intention to use TCM. TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
| Variable | Categories | Case | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 212 | 42.91 |
| Male | 282 | 57.09 | |
| Age | 30 or below | 62 | 12.55 |
| 31-45 | 288 | 58.30 | |
| 46-60 | 134 | 27.13 | |
| 60 or above | 10 | 2.02 | |
| Marital status | Unmarried | 44 | 8.91 |
| Married | 450 | 91.09 | |
| Family register | Rural | 28 | 5.67 |
| Urban | 466 | 94.33 | |
| Educational level | Secondary or below | 22 | 4.45 |
| Tertiary or above | 472 | 95.55 | |
| Family annual income (RMB) | 50 000 or below | 52 | 10.53 |
| 50 000-200 000 | 348 | 70.45 | |
| 200 000 or above | 94 | 19.02 | |
| Occupational background | Western Medicine | 246 | 49.80 |
| Traditional Chinese Medicine | 248 | 50.20 |
Table 1 Descriptive statistics of demographic characteristics
| Variable | Categories | Case | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 212 | 42.91 |
| Male | 282 | 57.09 | |
| Age | 30 or below | 62 | 12.55 |
| 31-45 | 288 | 58.30 | |
| 46-60 | 134 | 27.13 | |
| 60 or above | 10 | 2.02 | |
| Marital status | Unmarried | 44 | 8.91 |
| Married | 450 | 91.09 | |
| Family register | Rural | 28 | 5.67 |
| Urban | 466 | 94.33 | |
| Educational level | Secondary or below | 22 | 4.45 |
| Tertiary or above | 472 | 95.55 | |
| Family annual income (RMB) | 50 000 or below | 52 | 10.53 |
| 50 000-200 000 | 348 | 70.45 | |
| 200 000 or above | 94 | 19.02 | |
| Occupational background | Western Medicine | 246 | 49.80 |
| Traditional Chinese Medicine | 248 | 50.20 |
| Parameter | Item | Standard loading | AVE | CR | Cronbach’s α | Bartlett Test of Sphericity | KMO Measure | Square root of AVE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognition (C) | C1 | 0.735 | 0.583 | 0.906 | 0.915 | 2607.352 | 0.858 | 0.764 | |
| C2 | 0.735 | ||||||||
| C3 | 0.874 | ||||||||
| C4 | 0.890 | ||||||||
| C5 | 0.695 | ||||||||
| C6 | 0.622 | ||||||||
| C7 | 0.760 | ||||||||
| Attitude (ATT) | ATT1 | 0.886 | 0.764 | 0.907 | 0.911 | 1228.996 | 0.767 | 0.874 | |
| ATT2 | 0.888 | ||||||||
| ATT3 | 0.848 | ||||||||
| Subjective norms (SN) | SN1 | 0.951 | 0.871 | 0.964 | 0.960 | 2508.428 | 0.860 | 0.933 | |
| SN2 | 0.965 | ||||||||
| SN3 | 0.936 | ||||||||
| SN4 | 0.878 | ||||||||
| Perceived behavioral control (PBC) | PBC1 | 0.824 | 0.727 | 0.941 | 0.936 | 2647.807 | 0.906 | 0.853 | |
| PBC2 | 0.768 | ||||||||
| PBC3 | 0.897 | ||||||||
| PBC4 | 0.827 | ||||||||
| PBC5 | 0.884 | ||||||||
| PBC6 | 0.907 | ||||||||
| Past behavior (PB) | PB1 | 0.925 | 0.789 | 0.918 | 0.859 | 1068.051 | 0.755 | 0.888 | |
| PB2 | 0.868 | ||||||||
| PB3 | 0.870 | ||||||||
| Behavioral intention (BI) | BI1 | 0.944 | 0.872 | 0.932 | 0.948 | 879.793 | 0.500 | 0.934 | |
| BI2 | 0.924 | ||||||||
Table 2 Reliability and validity analysis results of the measurement model
| Parameter | Item | Standard loading | AVE | CR | Cronbach’s α | Bartlett Test of Sphericity | KMO Measure | Square root of AVE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognition (C) | C1 | 0.735 | 0.583 | 0.906 | 0.915 | 2607.352 | 0.858 | 0.764 | |
| C2 | 0.735 | ||||||||
| C3 | 0.874 | ||||||||
| C4 | 0.890 | ||||||||
| C5 | 0.695 | ||||||||
| C6 | 0.622 | ||||||||
| C7 | 0.760 | ||||||||
| Attitude (ATT) | ATT1 | 0.886 | 0.764 | 0.907 | 0.911 | 1228.996 | 0.767 | 0.874 | |
| ATT2 | 0.888 | ||||||||
| ATT3 | 0.848 | ||||||||
| Subjective norms (SN) | SN1 | 0.951 | 0.871 | 0.964 | 0.960 | 2508.428 | 0.860 | 0.933 | |
| SN2 | 0.965 | ||||||||
| SN3 | 0.936 | ||||||||
| SN4 | 0.878 | ||||||||
| Perceived behavioral control (PBC) | PBC1 | 0.824 | 0.727 | 0.941 | 0.936 | 2647.807 | 0.906 | 0.853 | |
| PBC2 | 0.768 | ||||||||
| PBC3 | 0.897 | ||||||||
| PBC4 | 0.827 | ||||||||
| PBC5 | 0.884 | ||||||||
| PBC6 | 0.907 | ||||||||
| Past behavior (PB) | PB1 | 0.925 | 0.789 | 0.918 | 0.859 | 1068.051 | 0.755 | 0.888 | |
| PB2 | 0.868 | ||||||||
| PB3 | 0.870 | ||||||||
| Behavioral intention (BI) | BI1 | 0.944 | 0.872 | 0.932 | 0.948 | 879.793 | 0.500 | 0.934 | |
| BI2 | 0.924 | ||||||||
| Mean ± SD | ATT | BI | SN | PB | PBC | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATT | 4.3±0.8 | 0.874 | |||||
| BI | 4.2±0.9 | 0.824a | 0.934 | ||||
| SN | 4.0±0.9 | 0.712a | 0.753a | 0.933 | |||
| PB | 4.0±1.1 | 0.725a | 0.782a | 0.692a | 0.888 | ||
| PBC | 4.1±0.8 | 0.756a | 0.772a | 0.795a | 0.723a | 0.853 | |
| C | 3.8±0.7 | 0.748a | 0.682a | 0.606a | 0.567a | 0.567a | 0.764 |
Table 3 Descriptive statistics, correlation and discriminative validity analysis results
| Mean ± SD | ATT | BI | SN | PB | PBC | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATT | 4.3±0.8 | 0.874 | |||||
| BI | 4.2±0.9 | 0.824a | 0.934 | ||||
| SN | 4.0±0.9 | 0.712a | 0.753a | 0.933 | |||
| PB | 4.0±1.1 | 0.725a | 0.782a | 0.692a | 0.888 | ||
| PBC | 4.1±0.8 | 0.756a | 0.772a | 0.795a | 0.723a | 0.853 | |
| C | 3.8±0.7 | 0.748a | 0.682a | 0.606a | 0.567a | 0.567a | 0.764 |
| Dimension | Western physicians (n = 246) | TCM physicians (n = 248) | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BI | 3.8±0.8 | 4.6±0.6 | –12.695 | <0.001 |
| ATT | 3.9±0.8 | 4.7±0.5 | –12.405 | <0.001 |
| SN | 3.6±0.9 | 4.4±0.7 | –10.880 | <0.001 |
| PBC | 3.75±0.8 | 4.5±0.6 | –12.001 | <0.001 |
| C | 3.6±0.7 | 4.0±0.5 | –8.159 | <0.001 |
| PB | 3.3±1.0 | 4.5±0.8 | –13.780 | <0.001 |
Table 4 Differences in each variable between TCM and Western physicians ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Dimension | Western physicians (n = 246) | TCM physicians (n = 248) | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BI | 3.8±0.8 | 4.6±0.6 | –12.695 | <0.001 |
| ATT | 3.9±0.8 | 4.7±0.5 | –12.405 | <0.001 |
| SN | 3.6±0.9 | 4.4±0.7 | –10.880 | <0.001 |
| PBC | 3.75±0.8 | 4.5±0.6 | –12.001 | <0.001 |
| C | 3.6±0.7 | 4.0±0.5 | –8.159 | <0.001 |
| PB | 3.3±1.0 | 4.5±0.8 | –13.780 | <0.001 |
| Fitness index | Absolute fitness index | Value-added fitness index | Parsimonious fitness index | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2/df | RMSEA | GFI | AGFI | NFI | IFI | CFI | PNFI | PGFI | PCFI | |||
| Criteria | < 5.00 | < 0.10 | > 0.80 | > 0.80 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.50 | > 0.50 | > 0.50 | ||
| Results | 4.820 | 0.088 | 0.844 | 0.808 | 0.910 | 0.927 | 0.927 | 0.804 | 0.688 | 0.819 | ||
Table 5 Structural equation model fitting index analysis results
| Fitness index | Absolute fitness index | Value-added fitness index | Parsimonious fitness index | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2/df | RMSEA | GFI | AGFI | NFI | IFI | CFI | PNFI | PGFI | PCFI | |||
| Criteria | < 5.00 | < 0.10 | > 0.80 | > 0.80 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.50 | > 0.50 | > 0.50 | ||
| Results | 4.820 | 0.088 | 0.844 | 0.808 | 0.910 | 0.927 | 0.927 | 0.804 | 0.688 | 0.819 | ||
| Hypothesis | Standardized coefficients (β) | SE | t value | P value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1: ATT ← C | 0.606 | 0.052 | 14.967 | a | Supported |
| H2: BI ← ATT | 0.467 | 0.051 | 10.341 | a | Supported |
| H3: BI ← SN | 0.177 | 0.043 | 3.301 | a | Supported |
| H4: BI ← PBC | 0.384 | 0.023 | 11.366 | a | Supported |
| H5: ATT ← SN | 0.569 | 0.05 | 9.326 | a | Supported |
| H6: ATT ← PBC | 0.064 | 0.041 | 1.118 | 0.263 | No Supported |
| H7: BI ← PB | 0.133 | 0.056 | 2.184 | b | Supported |
Table 6 Results of structural equation modeling analysis
| Hypothesis | Standardized coefficients (β) | SE | t value | P value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1: ATT ← C | 0.606 | 0.052 | 14.967 | a | Supported |
| H2: BI ← ATT | 0.467 | 0.051 | 10.341 | a | Supported |
| H3: BI ← SN | 0.177 | 0.043 | 3.301 | a | Supported |
| H4: BI ← PBC | 0.384 | 0.023 | 11.366 | a | Supported |
| H5: ATT ← SN | 0.569 | 0.05 | 9.326 | a | Supported |
| H6: ATT ← PBC | 0.064 | 0.041 | 1.118 | 0.263 | No Supported |
| H7: BI ← PB | 0.133 | 0.056 | 2.184 | b | Supported |
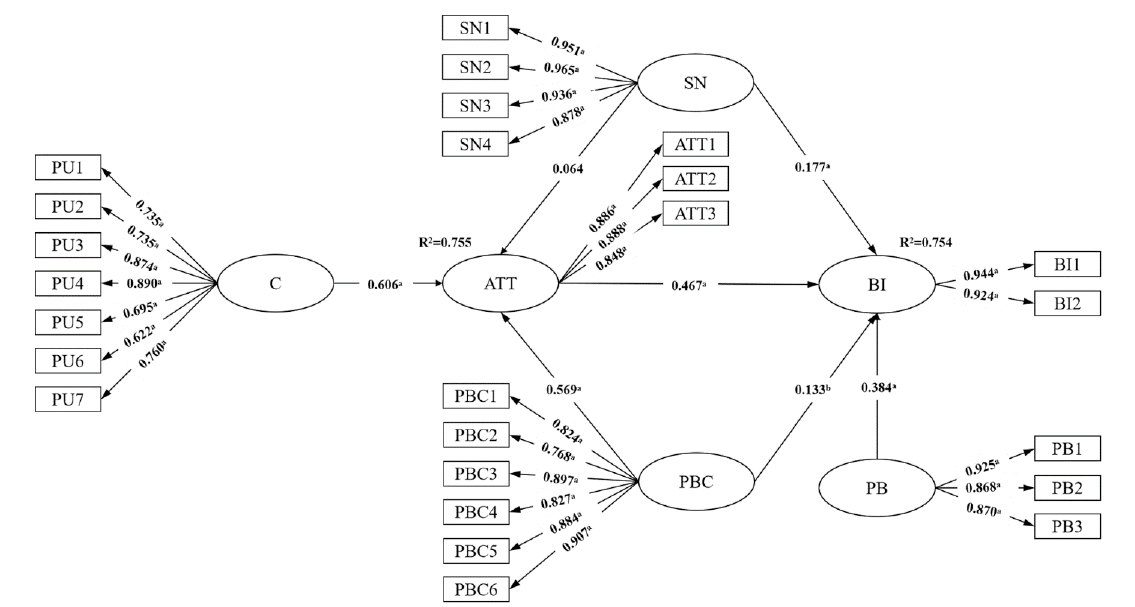
Figure 2 Structural equation model on intention of TCM utilization based on TPB C: cognition; ATT: attitude; SN: subjective norms; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; PBC: perceived behavioral control; PB: past behavior; BI: behavior intention; standardized path coefficients were presented; aP < 0.001; bP < 0.05.
| Dependent variable | Independent variable | B | SEB | β | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Behavior intention | Gender | 0.027 | 0.069 | 0.016 | 0.395 | 0.693 |
| Age | 0.069 | 0.050 | 0.058 | 1.376 | 0.169 | |
| Marital status | 0.172 | 0.130 | 0.057 | 1.327 | 0.185 | |
| Family register | 0.054 | 0.156 | 0.014 | 0.345 | 0.730 | |
| Educational level | –0.175 | 0.171 | –0.042 | –1.026 | 0.306 | |
| Family annual income | –0.077 | 0.069 | –0.045 | –1.113 | 0.266 | |
| Occupational background | 0.866 | 0.068 | 0.502 | 12.824 | <0.001 |
Table 7 Regression analysis of demographics on TCM behavior intention and its components
| Dependent variable | Independent variable | B | SEB | β | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Behavior intention | Gender | 0.027 | 0.069 | 0.016 | 0.395 | 0.693 |
| Age | 0.069 | 0.050 | 0.058 | 1.376 | 0.169 | |
| Marital status | 0.172 | 0.130 | 0.057 | 1.327 | 0.185 | |
| Family register | 0.054 | 0.156 | 0.014 | 0.345 | 0.730 | |
| Educational level | –0.175 | 0.171 | –0.042 | –1.026 | 0.306 | |
| Family annual income | –0.077 | 0.069 | –0.045 | –1.113 | 0.266 | |
| Occupational background | 0.866 | 0.068 | 0.502 | 12.824 | <0.001 |
| 1 | Aleem A, Akbar Samad AB, Slenker AK. Emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2 and novel therapeutics against coronavirus (COVID-19). StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) online, 2022-05-12, cited 2022-06-10. 2022-06-10. Available from URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570580/. |
| 2 |
Awadasseid A, Wu Y, Tanaka Y, Zhang W. Current advances in the development of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17: 8-19.
DOI PMID |
| 3 | Tsai SC, Lu CC, Bau DT, et al. Approaches towards fighting the COVID-19 pandemic (Review). Int J Mol Med 2021; 47: 3-22. |
| 4 |
Shi YH, Huang YF, Wang WY, Yang L, Zhou H, Sang Z. Analysis on the current quality standards of Chinese materia medica used in COVID-19 prevention and treatment. Pharmacol Res 2020; 160: 105074.
DOI URL |
| 5 |
Zhou LP, Wang J, Xie RH, et al. The effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine as an auxiliary treatment for COVID-19: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Altern Complement Med 2021; 27: 225-37.
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Ren W, Liang P, Ma Y, et al. Research progress of Traditional Chinese Medicine against COVID-19. Biomed Pharmacother 2021; 137: 111310.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Ho LTF, Chan KKH, Chung VCH, Leung TH. Highlights of Traditional Chinese Medicine frontline expert advice in the China national guideline for COVID-19. Eur J Integr Med 2020; 36: 101116.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Chen KJ, Lu AP. Situation of integrative medicine in China: results from a national survey in 2004. Chin J Integr Med 2006; 12: 161-5.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Yu HY, Wang XQ, Zhang Y, Liu J, Lin HS. Application status of Chinese medicine on cancer rehabilitation: a preliminary questionnaire survey. Chin J Integr Med 2020; 26: 890-6.
DOI URL |
| 10 | Mcquade JL, Meng ZQ, Chen Z, et al. Utilization of and attitudes towards Traditional Chinese Medicine therapies in a Chinese cancer hospital: a survey of patients and physicians. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012; 2012: 504507. |
| 11 | Huber BM, Schoen-Angerer TV, Hasselmann O, Wildhaber J, Wolf U. Swiss paediatrician survey on complementary medicine. Swiss Med Wkly 2019; 149: w20091. |
| 12 |
Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organizational behavior and human decision processes 1991; 50: 179-211.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Lim HR, An S. Intention to purchase wellbeing food among Korean consumers: An application of the theory of planned behavior. Food Qual Prefer 2021; 88: 104101.
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Soorani F, Ahmadvand M. Determinants of consumers’ food management behavior: applying and extending the theory of planned behavior. Waste Management 2019; 98: 151-9.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Davis KC, Jacques-Tiura AJ, Stappenbeck CA, et al. Men’s condom use resistance: Alcohol effects on theory of planned behavior constructs. Health Psychol 2016; 35: 178-86.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Boissin C, Al Maniri AA, Al-Azri AS, Hasselberg M, Laflamme L. Determinants of speeding among new generations of car drivers from the Arabian Peninsula. An investigation based among Omani drivers using the theory of planned behaviour. PLoS One 2019, 14: e0226441.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Cheah I, Sadat Shimul A, Liang J, Phau I. Drivers and barriers toward reducing meat consumption. Appetite 2020; 149: 104636.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Bogers RP, Brug J, Assema PV, et al. Explaining fruit and vegetable consumption: The theory of planned behaviour and mis-conception of personal intake levels. Appetite 2004; 42: 157-66.
PMID |
| 19 | He Y, Yang F, Mu D, Xing Y, Li X. Examination of psychosocial predictors of Chinese hospital pharmacists’ intention to provide clinical pharmacy services using the theory of planned behaviour: a cross-sectional questionnaire study. BMJ Open 2016; 6: e012775. |
| 20 |
Muhammed A, Khuan L, Shariff-Ghazali S, Said SM, Hassan M. Predictors of midwives’ intention to provide planned home birth services to low-risk women: a theory of planned behaviour approach. Midwifery 2019; 73: 62-8.
DOI PMID |
| 21 |
Deng Q, Lu J, Zeng Z, Zheng Y, Liu W. Dynamics of Health Technology Diffusion in the Integrated Care System (DHTDICS): A development and validation study in China. Risk Manag Healthc Policy 2021; 14: 331-44.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Espada JP, Morales A, A Guillénriquelme, et al. Predicting condom use in adolescents: a test of three socio-cognitive models using a structural equation modeling approach. BMC Public Health 2016; 16: 35.
DOI PMID |
| 23 |
Shmueli L. Predicting intention to receive COVID-19 vaccine among the general population using the health belief model and the theory of planned behavior model. BMC Public Health 2021; 21: 84.
DOI URL |
| 24 | Hair JF, Babin BJ, Black WC, Anderson RE, Tatham RL. Multivariate data analysis., 6th ed. Upper Saddle River. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006: 460-1. |
| 25 |
Ouellette JA, Wood W. Habit and intention in everyday life: the multiple prodcess by which past behavior predicts future behavior. Psychol Bull 1998; 124: 54-7.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Wu Z, Jiang M, Li H, Luo X, Li X. Investigating the critical factors of professionals’ BIM sdoption behavior based on the theory of planned behavior. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021; 18: 3022.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Sun Y, Qin B, Hu Z, et al. Predicting mask-wearing behavior intention among international students during COVID-19 based on the theory of planned behavior. Ann Palliat Med 2021; 10: 3633647.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Chin WW, Gopal A, Salisbury WD. Advancing the theory of adaptive structuration: The development of a scale to measure faithfulness of appropriation. Inf Syst Res 1997; 8: 342-67.
DOI URL |
| 29 | Bagozzi RP, Yi Y. On the evaluation of structural equation models. JAMS 1988; 16: 74-94. |
| 30 |
Fornell C, Larcker DF. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: algebra and statistics. J Mark Res 1981; 18: 382-8.
DOI URL |
| 31 |
Doll WJ, Xia W, Torkzadeh G. A confirmatory factor analysis of the end-user computing satisfaction instrument. MIS Quarterly 1994; 18: 453-61.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Arpaci I, Baloğlu M. The impact of cultural collectivism on knowledge sharing among information technology majoring undergraduates. Comput Human Behav 2016; 56: 65-71.
DOI URL |
| 33 |
Bagheri Hosseinabadi M, Etemadinezhad S, Khanjani N, et al. Evaluating the relationship between job stress and job satisfaction among female hospital nurses in Babol: An application of structural equation modeling. Health Promot Perspect 2018; 8: 102-8.
DOI URL |
| 34 |
Dominguez LC, Silkens M, Sanabria A. The dutch residency educational climate test: construct and concurrent validation in Spanish language. Int J Med Educ 2019; 10: 138-48.
DOI URL |
| 35 |
Steiger JH. Structural model evaluation and modification: an interval estimation approach. Multivariate Behavioral Research 1990; 25: 173-80.
DOI PMID |
| 36 |
Deng Q, Zheng Y, Lu J, Zeng Z, Liu W. What factors predict physicians’ utilization behavior of contrast-enhanced ultrasound? Evidence from the integration of the theory of planned behavior and technology acceptance model using a structural equation modeling approach. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2021; 21: 173.
DOI URL |
| 37 |
Archambault P, Turcotte S, Smith PY, et al. Intention to use Wiki-based knowledge tools: survey of quebec emergency health professionals. JMIR Med Inform 2021; 9: e24649.
DOI URL |
| 38 |
Guo S, Guo X, Zhang X, Vogel D. Doctor-patient relationship strength’s impact in an online healthcare community. Inform Technol Dev 2018; 24: 279-300.
DOI URL |
| 39 | Guo S, Guo X, Fang Y, Vogel D. How doctors gain social and economic returns in online health-care communities: a professional capital perspective. J Manag Inform Sys 2017; 34: 487-519. |
| 40 |
Bamberg S, Möser G. Twenty years after Hines, Hungerford, and Tomera: a new Meta-analysis of psycho-social determinants of pro-environmental behaviour. J Environ Psychol 2007; 27: 14-25.
DOI URL |
| 41 |
Fornara F, Pattitoni P, Mura M, Strazzera E. Predicting intention to improve household energy efficiency: the role of value-belief-norm theory, normative and informational influence, and specific attitude. J Environ Psychol 2016; 45: 1-10.
DOI URL |
| 42 |
Xia Y, Shi LS, Chang JH, Miao HZ, Wang D. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on intention to use Traditional Chinese Medicine: a cross-sectional study based on the theory of planned behavior. J Integr Med 2021; 19: 219-25.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | FAN Rong, HE Haoyu, TANG Tao, CUI Hanjin. Long-term effects of Qingfei Paidu decoction (清肺排毒汤) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 acute pneumonia after treatment: a protocol for systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1068-1071. |
| [2] | SUN Wu, ZHAO Yuwei, LIAO Liang, ZHAO Zhonghui, CHEN Shiqi, YAN Xiaoling, WANG Xueyao, CHAO Guojun, ZHOU Jian. Effectiveness and safety of Xuebijing injection for patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 631-639. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yuehong, SHAO Xianzhi, ZHAO Qianlong, ZHAN Hualong, ZHANG Jianhua, DU Sisi, CHEN Jing, LIU Yingfang, ZHOU Haiwang, CHEN Xinsheng, HONG Ying, LIAN Fengmei, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness of Xiangsha Liujun pills (香砂六君丸) on decreased digestive function in convalescent patients of coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 552-558. |
| [4] | XU Guihua, CHEN Feifei, ZHANG Wei, WU Yingen, CHEN Xiaorong, SHI Kehua, WANG Zhenwei, SHI Miaoyan, ZHANG Xing, LU Yunfei, YUAN Weian, LYU Hua, CHEN Xuan. Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine on coronavirus disease 2019 in 92 patients: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 582-587. |
| [5] | YANG Cunqing, LIAN Fengmei, YANG Guiping, HUANG Yufeng, ZHANG Shuangbin, WANG Jianghua, ZHOU Jing, GUO Dongqing, SHEN Chuanyun, YE Tiansong, FU Aojie, LI Xiaoli, CHEN Le, ZHANG Huifeng, TU Qiyin, WANG Ying, YANG Wenzhe, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness of Xiaoyao capsule (逍遥丸) on sleep disorders and mood disturbance in patients in recovery from coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 343-351. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yuehong, DONG Dandan, YAN Youqin, ZHANG Hao, WANG Guangli, ZHOU Wei, LI Wei, QIU Li, LI Tingming, LIU Quan, XIA Ping, MAO Lina, YANG Danlin, YANG Lu, LIAN Fengmei, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness and safety of Jinshuibao capsules (金水宝胶囊) in treatment of residual cardiopulmonary symptoms in convalescent patients of coronavirus disease 2019: a pilot randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 134-139. |
| [7] | AN Xuedong, MAO Lina, XIA Ping, SU Wen, WANG Beibei, KOU Leiya, ZHANG Zequan, QI Meng, HU Song, CHEN Jing, LI Xiujuan, LIU Jinwei, ZHOU Juan, QIAO Jie, LUO Dan, LUO Guangwei, YAN Youqin, YANG Guiping, DONG Dandan, ZHOU Wei, TAO Junxiu, JIN De, TONG Xiaolin, WEI Li. Effects of Shengmai Yin (生脉饮) on pulmonary and cardiac function in coronavirus disease 2019 convalescent patients with cardiopulmonary symptoms: a randomized, double blind, multicenter control trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 140-145. |
| [8] | LI Ximeng, KANG Yuan, LI Wenjing, LIU Zhuangzhuang, XU Zhenlu, ZHANG Xiaoyu, CAI Runlan, GAO Yuan, QI Yun. Comparing the effects of three decoctions for coronavirus disease 2019 on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-related toll-like receptors-mediated inflammations [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 51-59. |
| [9] | ZHU Qingguang, ZHANG Shuaipan, LI Jingxian, SUN Wuquan, CHENG Wei, ZHAN Chao, CHENG Yanbin, FANG Lei, FANG Min. Effectiveness of Liu-zi-jue exercise on coronavirus disease 2019 in the patients: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 997-10053. |
| [10] | AN Xuedong, ZHANG Qing, TAO Junxiu, LI Li, CHEN Yun, LI Kejian, HE Jing, LIU Ru, GUO Juan, ZHANG Jia, ZHU Hui, LIAN Fengmei, LI Xiaodong. Shugan Jieyu capsule (舒肝解郁胶囊) improve sleep and emotional disorder in coronavirus disease 2019 convalescence patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 803-809. |
| [11] | ZHAO Yufeng, PANG Huaxin, Lü Lanting, ZHOU Pei, WANG Kaining, CAI Shengxing, ZHANG Huifeng, LI Kun. Risk assessment and analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine intervention in coronavirus disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 472-478. |
| [12] | XIA Wenguang, ZHENG Chanjuan, ZHANG Jixian, HUANG Min, LI Qinglin, DUAN Can, LI Zhengliang, FAN Cunyu, ZOU Yilong, XU Bo, YANG Fengwen, LIU Qingquan. Randomized controlled study of a diagnosis and treatment plan for moderate coronavirus disease 2019 that integrates Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 234-241. |
| [13] | YAN Shixing, Lü Yi, LIU Ziqing, REN Meng, HE Haiyang, XIAO Li, GUO Feng, PENG Miao, LI Xiaoxia, WANG Yong, XU Xi, YANG Tao, SHAO Zuoyu, HUANG Jingjing, XIAO Mingzhong. Mining intrinsic information of convalescent patients after suffering coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 279-288. |
| [14] | LI Li, AN Xuedong, ZHANG Qing, TAO Junxiu, HE Jing, CHEN Yun, LI Kejian, LIU Ru, GUO Juan, ZHANG Hao, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Shumian capsule(舒眠胶囊) improves symptoms of sleep mood disorder in convalescent patients of Corona Virus Disease 2019 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 974-981. |
| [15] | BAO Chunmiao, LI Binbin. Traditional Chinese Medicine enhances absorption of lung lesions in corona virus disease 2019 patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 982-984. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

