Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 556-564.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220519.004
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of Qihuang decoction (芪黄煎剂) on enteric nervous system in rats after gastrectomy
ZHANG Qi1,2, ZHENG Zhou1,2, HUANG Long1,2, PENG Hui1,2, YU Qingsheng1,2( ), WANG Laiyong1,2
), WANG Laiyong1,2
- 1 Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
2 Institute of Chinese Medicine Surgery, Anhui Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
-
Received:2021-08-26Accepted:2021-11-22Online:2022-08-15Published:2022-07-12 -
Contact:YU Qingsheng -
About author:Prof. YU Qingsheng, Department of General Surgery, First Affliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031; Institute of Chinese Medicine Surgery, Anhui Academy of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China. qsy6312@163.com, Telephone: +86-13866141906
-
Supported by:Investigate the Effect of Qihuang Decoction on Gastrointestinal Function and its Molecular Mechanism in Rats after Gastrectomy based on ENS-ICC-SMC Network Architecture(2020yfyzc02);Effect of Qihuang Decoction on Intestinal Lymphocyte Homing after Gastrectomy in Rats(81403406);Qihuang Decoction Inhibits Bacterial Migration during Gastrectomy in Rats and Regulates the M1-type Polarization of Macrophages induced by TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway based on lncRNA MALAT1 Sponge Mir-146a(82174160);Effects of Qihuang Decoction on Gastrointestinal Motility in Rats after Gastrectomy and its Molecular Mechanism were Studied based on ENS Framework(gxyq2019035);Investigate the Inhibition of Cryptotanshinone on 5-FU-SGC-7901 Human Gastric Cancer Cells and its Mechanism based on JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway(2008085MH266)
Cite this article
ZHANG Qi, ZHENG Zhou, HUANG Long, PENG Hui, YU Qingsheng, WANG Laiyong. Efficacy of Qihuang decoction (芪黄煎剂) on enteric nervous system in rats after gastrectomy[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 556-564.
share this article
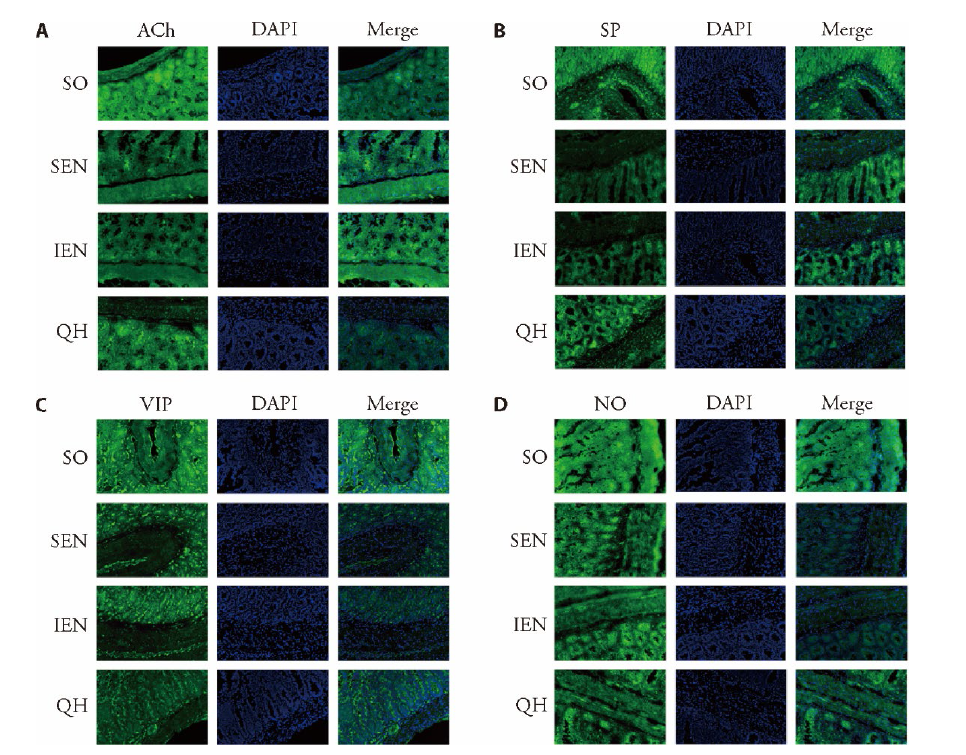
Figure 2 Morphology and distribution of enteric neuronal cells under confocal laser scanning microscopy (× 200) A-D: the immunofluorescence of enteric neuronal cells (× 200). A: the ACh neuron in different groups; B: the SP neuron in different groups; C: the VIP neuron in different groups; D: the NO neuron in different groups. SO group: sham operation group, sham operated (n = 5); SEM group: standard enteral nutrition group, gastrectomy rats treated with Fresubin at a dose of 120 kJ·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5); IEM group: immune enteral nutrition group, gastrectomy rats treated with Supportan at a dose of 120 kJ·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5); QH group: Qihuang decoction group, gastrectomy rats treated with Qihuang decoction at a dose of 10 g·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5). ACh: acetylcholine; SP: substance P; VIP: vasoactive intestinal peptide; NO: nitric oxide.
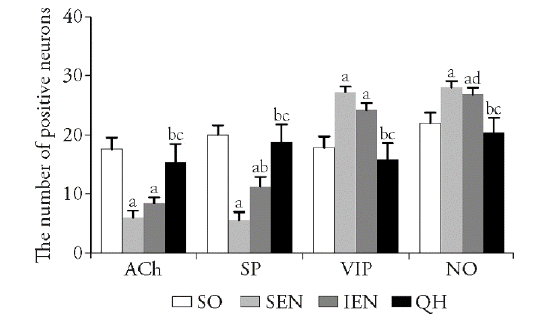
Figure 3 Number of positive neurons SO group: sham operation group, sham operated (n = 5); SEM group: standard enteral nutrition group, gastrectomy rats treated with Fresubin at a dose of 120 kJ·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5); IEM group: immune enteral nutrition group, gastrectomy rats treated with Supportan at a dose of 120 kJ·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5); QH group: Qihuang decoction group, gastrectomy rats treated with Qihuang decoction at a dose of 10 g·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5). aP < 0.01 compared with the SO group. bP < 0.01and dP < 0.05compared with the SEN group cP < 0.01 compared with the IEM group. ACh: acetylcholine; SP: substance P; VIP: vasoactive intestinal peptide; NO: nitric oxide.

Figure 4 mRNA transcription of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors SO group: sham operation group, sham operated (n = 5); SEM group: standard enteral nutrition group, gastrectomy rats treated with Fresubin at a dose of 120 kJ·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5); IEM group: immune enteral nutrition group, gastrectomy rats treated with Supportan at a dose of 120 kJ·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5); QH group: Qihuang decoction group, gastrectomy rats treated with Qihuang decoction at a dose of 10 g·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5). aP < 0.01 and eP < 0.05, compared with the SO group; bP < 0.01and dP < 0.05, compared with the SEN group; cP < 0.01 and fP < 0.05, compared with the IEM group. AChE: acetylcholinesterase; SP: substance P; VIP: vasoactive intestinal peptide; NOS: nitric oxide synthase; M3R: muscarinic acetylcholine receptors; VIP2R: vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor; NK1R: peptidergic neuron receptor.
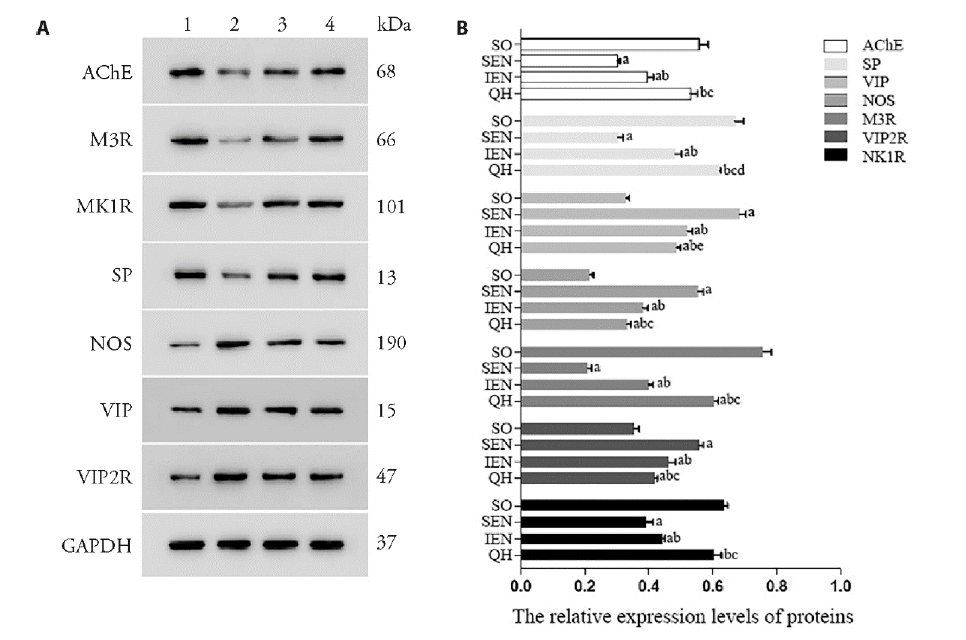
Figure 5 Protein expression of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors A: AChE, M3R, NK1R, SP, NOS, VIP, VIP2R and GAPDH protein expression in SO group (1), SEN group (2), IEN group (3) and QH group (4); B: AChE, M3R, NK1R, SP, NOS, VIP and VIP2R relative protein expression levels in SO group, SEN group, IEN group and QH group. SO group: sham operation group, sham operated (n = 5); SEM group: standard enteral nutrition group, gastrectomy rats treated with Fresubin at a dose of 120 kJ·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5); IEM group: immune enteral nutrition group, gastrectomy rats treated with Supportan at a dose of 120 kJ·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5); QH group: Qihuang decoction group, gastrectomy rats treated with Qihuang decoction at a dose of 10 g·kg-1·d-1, lasted for 7 d (n = 5). aP < 0.01 and dP < 0.05, compared with the SO group. bP < 0.01, compared with the SEN group. cP < 0.01 and eP < 0.05, compared with the IEM group. SP: substance P; VIP: vasoactive intestinal peptide; NOS: nitric oxide synthase; M3R: muscarinic acetylcholine receptors; VIP2R: vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor; NK1R: peptidergic neuron receptor.
| 1 | Furness JB, Costa M. The enteric nervous system. New York: Churchill Livingstone 1988; 94: 549-50. |
| 2 | Gershon MD, Kirchgessner AL, Wade PR. Functional anatomy of the enteric nervous system. In: Johnson LR, ed. Physiology of the gastrointestinaltract. 3rd ed. New York: Raven Press, 1994: 381-422. |
| 3 |
Goyal RK, Hirano I. The enteric nervous system. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 1106-15.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
Hansen MB. The enteric nervous system II: gastrointestinal functions. Pharmacol Toxicol 2003; 92: 249-57.
DOI URL |
| 5 | Reddy PM. Effects of the autonomic nervous system, central nervous system and enteric nervous system on gastrointestinal motility. East Cent Afr J Pharm Sci 2010; 13: 50-7. |
| 6 |
Kalff C, Schraut WH, Billiar TR, et al. Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in postoperative intestinal smooth muscle dysfunction in rodents. Gastroenterology 2000; 118: 316-27.
PMID |
| 7 |
Mans E, Serra-Prat M, Palomera E, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy effects on hunger, satiation, and gastrointestinal hormone and motility responses after a liquid meal test. Am J Clin Nutr 2015; 102: 540-47.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Endo M, Hori M, Ozaki H, et al. Daikenchuto, a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, ameliorates postoperative ileus by anti-inflammatory action through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Gastroenterol 2014; 49: 1026-39.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018; 68: 394-24.
DOI URL |
| 10 | Gu QH, Hu B, Zhang XD, et al. Clinical observation on Xiaotan Sanjie formula combined with chemotherapy for 32 cases of advanced gastric cancer. J Tradit Chin Med 2013; 54: 2008-2011. |
| 11 | Ruan YP, Liu YX, Yao L. Influence of Yiqi Bushen Formula on the ability of invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells. J Tradit Chin Med 2012; 53: 148-50 |
| 12 |
Hu Y, Huang C, Sun Y, et al. Morbidity and mortality of laparoscopic versus open D2 distal gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol 2016; 34: 1350-57.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Javed I, Jhuma S. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and sepsis - an ever-evolving paradigm. Indian J Pediatr 2015; 82: 675-76.
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Long L, Wang J, Deng Y, et al. Curcumin ameliorates reserpine-induced gastrointestinal mucosal lesions through inhibiting IκB-α/NF-κB pathway and regulating expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide and gastrin in rats. J Med Food 2016; 19: 528-34.
DOI URL |
| 15 | Cong W, Pan Z, Yanan Z, et al. Chinese rice wine inhibits contraction activity of the isolated rat small intestine through intestinal myenteric plexus. Food Sci 2019; 40: 173-8. |
| 16 | Shaorong Z, Lannong J, Jiangen Y, et al. The effect of Shunqi Tongfu mixture on plasma levels of gastrointestinal hormones in rats with gastrointestinal motility disorder. Yunnan Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2015; 38: 10-2. |
| 17 | Yuxiang Z. The effect of modified Wumo decoction on slow transit constipation and the level of substance P, vasoactive intestinal peptide, nitric oxide and neuropeptide Y in serum. Zhong Guo Lao Nian Xue Za Zhi 2016; 8: 4008-9. |
| 18 | Yu C, Hangjun G, Gan H, et al. Clinical study on Amomum villosum’s promotion of gastrointestinal function recovery after gastric operation. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2019; 28: 19-22. |
| 19 | Chen ZQ, Cao LX, Shang WF, et al. The effect of Xiangbin Fang (香槟方) on gastrointestinal motility of dogs after abdominal operation. J Tradit Chin Med 2015; 2: 1953-57. |
| 20 | Xiong LH, Su PP, Wang Z. Research on prescription of Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome based on the ancient books. J Tradit Chin Med 2015; 56: 1645-47. |
| 21 | Liu YC, Yu QS. Effect of early use of medicinal herbs through intestinal canal on gastrointestinal peristalsis after gastric cancer operation. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Wai Ke Za Zhi 2008; 14: 538-41. |
| 22 | Yu QS, Zheng Z, Peng H, et al. Effect of Qihuang decoction combined with enteral nutrition on postoperative gastric cancer of nutrition and immune function. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 1795107. |
| 23 |
Peng H, Shen Y, Zhang Q, et al. Qihuang decoction promotes the recovery of intestinal immune barrier dysfunction after gastrectomy in rats. Am J Transl Res 2018; 10: 827-36.
PMID |
| 24 | Zhang Q, Cheng L, Huang L, et al. Enhanced intestinal lymphocyte homing intervention using Qihuang decoction intestinal instillation in rats after gastrectomy. Int J Clin Exp Med 2020; 13: 5790-8. |
| 25 | Yu QS, Zhang Q, Pan JF, et al. Effects of Qihuang decoction on immunity function and bowel mucosal barrier on early days after gastric cancer operation in rats. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Wai Ke Za Zhi 2009; 15: 135-8. |
| 26 |
Walsh KT, Zemper AE. The enteric nervous system for epithelial researchers: basic anatomy, techniques, and interactions with the epithelium. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepato 2019; 8: 369-78.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Kirchgessner AL, Gershon MD. Innervation of the pancreas by neurons in the gut. J Neurosci 1990; 10: 1626-42.
PMID |
| 28 | Szurszewski JH, Miller SM. Physiology of prevertebral ganglia. In: Johnson LR, editor. Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. 3rd ed. New York: Raven Press, 1994: 795-878. |
| 29 |
Worl J, Mayer B, Neuhuber WL. Nitrergic innervation of the rat esophagus: focus on motor endplates. J Auton Nerv Syst 1994; 49: 227-33.
DOI URL |
| 30 | Gabella G. Structure of muscles and nerves in the gastrointestinal tract. In: Johnson LR, editor. Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. 3rd ed. New York: Raven Press, 1994: 751-94. |
| 31 |
Gershon Michael D. Nerves, reflexes, and the enteric nervous system: pathogenesis of the irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol 2005; 39: S184-93.
DOI PMID |
| 32 |
Russell John P, Mohammadi E, Ligon C, et al. Enteric RET inhibition attenuates gastrointestinal secretion and motility via cholinergic signaling in rat colonic mucosal preparations. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2019; 31: e13479.
DOI URL |
| 33 |
Turner DJ, Martin PC, Rao JN, et al. Substance P regulates migration in rat intestinal epithelial cells. Ann Surg 2007; 245: 408-14.
DOI URL |
| 34 |
Majkowska-Pilip A, Halik PK. The Significance of NK1 receptor ligands and their application in targeted radionuclide tumour therapy. Pharmaceutics 2019; 11: 1-28.
DOI URL |
| 35 | Lissak K, Eedroczi E. Effect of cortical denervation upon acetylcholin-cholinesterase system and excitability of the central nervous system. Acta Physiol Hung 1952; 3: 39-48. |
| 36 |
Fu XY, Li Z, Zhang N, et al. Effects of gastrointestinal motility on obesity. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2014; 11: 3.
DOI URL |
| 37 | Schwerdtfeger LA. Vasoactive intestinal peptide regulates ileal goblet cell production in mice. Physiol Rep 2020; 8: e14363. |
| 38 |
Guerra DD, Bok R, Lorca RA. Protein kinase A facilitates relaxation of mouse ileum via phosphorylation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Br J Pharmacol 2020; 177: 2765-78.
DOI URL |
| 39 |
Hogan S, Steffens D, Rangan A, et al. The effect of diets delivered into the gastrointestinal tract on gut motility after colorectal surgery-a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr 2019; 73: 1331-42.
DOI URL |
| 40 | Xiu ZC, Chen Q, Shang WF. Discussion on VIP/NO signal transduction mechanisms of abnormal small intestine function of spleen-deficiency syndrome. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2006; 40: 55-6. |
| 41 | Pan HS, Zhong GL, Qiu WM, et al. Effect of Buzhong Yiqi decoction on gastrointestinal function of exercise-induced fatigue rats. Guangzhou Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2013; 30: 864-7. |
| [1] | Hou Lili, Xu Lei, Shi Yan, Gu Fen. Effect of electric acupoint stimulation on gastrointestinal hormones and motility among geriatric postoperative patients with gastrointestinal tumors [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(04): 450-455. |
| [2] | Xu Zejun, Xu Cuiping, Ge Hongxia, Li Yan, Chu Liangliang, Zhang Jie, Cheng Kelin. Modified Dachengqi Tang improves decreased gastrointestinal motility in postoperative esophageal cancer patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(03): 249-254. |
| [3] | Zhao Yuxue, Cui Changxiang, Qin Qingguang, Ben Hui, Gao Junhong, Yu Xiaochun, Zhu Bing. Effect of manual acupuncture on bowel motility in normal kunming mouse [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(02): 227-233. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||