Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 586-594.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.04.004
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Exploring the mechanism of hirudin in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease using network pharmacology combined with molecular docking verification
PANG Xinxin, ZHU Qing, PENG Zining, ZHANG Yage, SHI Xiujie, HAN Jiarui( )
)
- Department of Nephropathy, Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, China
-
Received:2021-04-06Accepted:2021-07-26Online:2022-08-15Published:2022-07-12 -
Contact:HAN Jiarui -
About author:HAN Jiarui, Department of Nephropathy, Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, China. HanJR2018@126.com, Telephone: +86-371-60979837
-
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province(202300410256);Research Project of the National TCM Clinical Research Base(2019JDZX2119);Key R & D and Extension Project in Henan Province(202102310505);Key R & D and Extension Project in Henan Province(202102310171)
Cite this article
PANG Xinxin, ZHU Qing, PENG Zining, ZHANG Yage, SHI Xiujie, HAN Jiarui. Exploring the mechanism of hirudin in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease using network pharmacology combined with molecular docking verification[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 586-594.
share this article

Figure 2 PPI relationship diagram of hirudin and DKD Different color lines between nodes represent different interactions. Yellow: protein interaction; black: gene co-expression; light blue: protein homology; dark blue: gene co-evolution; red: gene fusion; green: gene pro-connection. PPI: protein-protein interaction; DKD: diabetic kidney disease.

Figure 4 Related biological functions of hirudin in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease "count" values represent the number of targets associated with the biological function, and P adjust indicate significance.
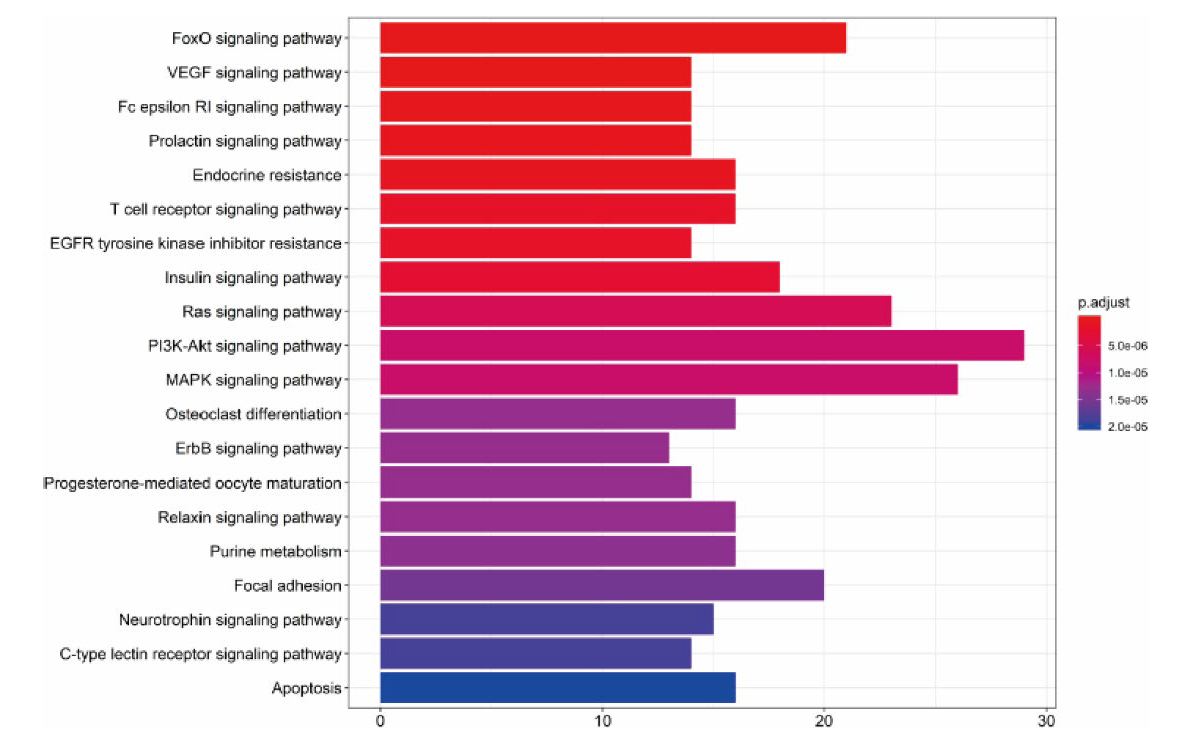
Figure 5 Key signaling pathway of hirudin in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease Red indicates the target of hirudin on signaling pathway (the original image is from Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway database).
| No. | Gene symbol | Gene ID | PDB ID | Hydrogen number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Serum albumin | ALB | 6HSC | 3 |
| 2 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | AKT1 | 1UNQ | 6 |
| 3 | Epidermal growth factor receptor | EGFR | 4LQM | 3 |
| 4 | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | SRC | 2IIM | 3 |
| 5 | Catalase | CAT | 1DGB | 6 |
| 6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 | MAPK8 | 4QTD | 3 |
| 7 | Caspase-3 | CASP3 | 3KJF | 5 |
| 8 | GTPase HRas | HRAS | 4XVR | 2 |
| 9 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | HSP90AA1 | 4YKZ | 5 |
| 10 | Estrogen receptor | ESR1 | 5AAV | 3 |
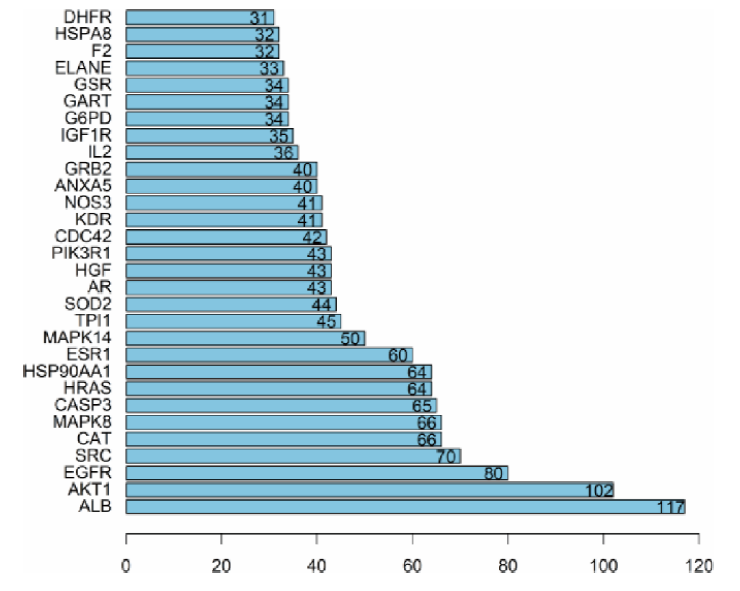
Table 1 Molecular docking data of the core target of diabetic kidney disease treated by hirudin
| No. | Gene symbol | Gene ID | PDB ID | Hydrogen number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Serum albumin | ALB | 6HSC | 3 |
| 2 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | AKT1 | 1UNQ | 6 |
| 3 | Epidermal growth factor receptor | EGFR | 4LQM | 3 |
| 4 | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | SRC | 2IIM | 3 |
| 5 | Catalase | CAT | 1DGB | 6 |
| 6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 | MAPK8 | 4QTD | 3 |
| 7 | Caspase-3 | CASP3 | 3KJF | 5 |
| 8 | GTPase HRas | HRAS | 4XVR | 2 |
| 9 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | HSP90AA1 | 4YKZ | 5 |
| 10 | Estrogen receptor | ESR1 | 5AAV | 3 |

Figure 6 Optimal binding mode of the main active component of hirudin and the key target protein of diabetic kidney disease a-j of them correspond to the molecular docking diagrams of 1-10 proteins bound to hirudin in Table 1, respectively.
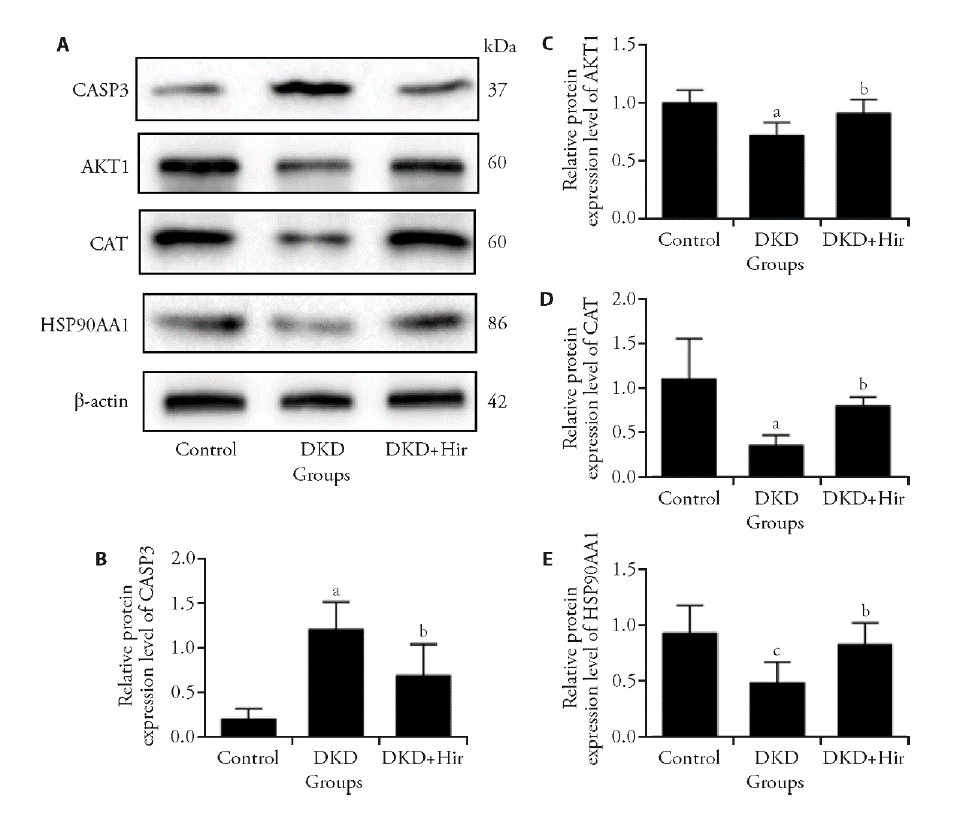
Figure 7 Effects of hirudin on protein expression levels of CASP3, AKT1, CAT and HSP90AA1 in renal tissues of DKD rats A: representative images of Western blots. B-E: relative expression of CASP3, AKT1, CAT and HSP90AA1 in renal tissues of DKD rats. CASP3: caspase-3; AKT1: RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; CAT: Catalase; HSP90AA1: Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha;β-actin was applied as control protein. Rats in Control group were given intraperitoneal injection of normal saline; Rats in DKD group were given intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg/kg streptozotocin; Rats in DKD + hirudin group were administered 5 U hirudin by subcutaneous injection. Compared with the normal control group, aP < 0.01, cP < 0.05, and compared with the DKD group, bP < 0.05.
| 1 | Ding XQ, Zhu JM. Research progress, existing problems and prospect of the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Shanghai Yi Xue 2018; 41: 73-7. |
| 2 | Mu X zhuang AW, Ma GL, et al. Cluster analysis of TCM syndromes in 237 patients with clinical stage diabetic nephropathy. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2016; 34: 332-5. |
| 3 | Guo Q, Chen ZQ, Fang J, et al. Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine for removing blood stasis and collaterals on laboratory indexes related to collaterals of diabetic nephropathy rats. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2016; 31: 5188-91. |
| 4 | Yan YY, Pan SY, Lin BJ, et al. Effects of natural hirudin on the angiogenesis of ischemic flaps in rats. Zhong Guo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 2020; 34: 382-6. |
| 5 |
Pang XX, Zhang YG, Peng ZN, et al. Hirudin reduces nephropathy microangiopathy in STZ-induced diabetes rats by inhibiting endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. Life Sci 2020; 255: 117779.
DOI URL |
| 6 | Pang XX, Zhang YG, Shi XJ, et al. Hirudin reduces the expression of markers of the extracellular matrix in renal tubular epithelial cells in a rat model of diabetic kidney disease through the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit 2020; 26: e921894. |
| 7 | Wang X, Shen Y, Wang S, et al. PharmMapper 2017 update: a web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res 2017; 45: 356-60. |
| 8 | Stelzer G, Rosen N, Plaschkes I, et al. The genecards suite: from gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 2016; 54: 1-30. |
| 9 |
Amberger JS, Bocchini CA, Schiettecatte F, et al. OMIM.org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res 2015; 43: 789-98.
DOI PMID |
| 10 |
Piñero J, Ramírez-Anguita JM, Saüch-Pitarch J, et al. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2020; 48: 845-55.
DOI PMID |
| 11 | Law V, Knox C, Djoumbou Y, et al. DrugBank 4.0: shedding new light on drug metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42: 1091-7. |
| 12 |
Thomas MC, Brownlee M, Susztak K, et al. Diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015; 1: 15018.
DOI URL |
| 13 | Xiao Y, Zhao JX. Zhao Jin-xi's experience in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2018; 33: 159-62. |
| 14 | Tong XL, Zhou Q, Zhao LH, et al. Experience of differentiation and treatment of diabetic nephropathy in Chinese medicine. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2014; 29: 144-6. |
| 15 | Pang XX, Tong Y, Li XP, et al. Research progress of leech and its extract in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Guang Ming Zhong Yi 2019; 34: 168-71. |
| 16 |
Han JR, Pang XX, Zhang YG, et al. Hirudin protects against kidney damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rats by inhibiting inflammation via P38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther 2020; 14: 3223-34.
DOI URL |
| 17 | Fan L, Dong ZH, Yang HX, et al. Study on the mechanism of hirudin alleviating human renal tubular epithelial cell fibrosis through JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Zhong Yao Cai 2018; 41: 982-5. |
| 18 | Xie J, Gao S, Li L, et al. Research progress and application strategy of network pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhong Cao Yao 2019; 50: 2257-65. |
| 19 | Wu DP, Xiao Y, Zhang YY, et al. Regulation of the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway on autophagy in diabetic rat renal tissue. Zhong Yi Sheng Li Bing Li Za Zhi 2016; 32: 2015-9. |
| 20 | Feng M, Teng WH, Jiang WW, et al. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in cardiovascular remodeling in rats with renal vascular hypertension. Zhong Guo Yao Li Xue Tong Bao 2016; 32: 625-31. |
| 21 |
Hwang I, Lee J, Huh JY, et al. Catalase deficiency accelerates diabetic renal injury through peroxisomal dysfunction. Diabetes 2012; 61: 728-38.
DOI PMID |
| 22 | Wang M, Wang Q, Wang Z, et al. The molecular evolutionary patterns of the insulin/FOXO signaling pathway. Evol Bioinform Online 2013; 9: 1-16. |
| 23 | Lee S, Dong HH. FoxO integration of insulin signaling with glucose and lipid metabolism. J Endocrinol 2017; 233: 67-79. |
| 24 | Wang XM, Yao M, Liu SX, et al. Interplay between the Notch and PI3K/Akt pathways in high glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2014; 306: 205-13. |
| 25 | Li CF, Cao YD, LI H, et al. Effect of combined treatment of senile diabetic nephropathy on inflammatory factors and pi3K-Akt path-ay in mononuclear cells. Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018; 34: 683-9. |
| 26 |
Declèves AE, Sharma K. Novel targets of antifibrotic and anti-inf-lammatory treatment in CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol 2014; 10: 257-67.
DOI URL |
| 27 | Melincovici CS, Boşca AB, Şuşman S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol 2018; 59: 455-67. |
| 28 |
Lan A, Du J. Potential role of Akt signaling in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2015; 30: 385-94.
DOI URL |
| 29 | Kim IY, Lee MY, Park MW, et al. Deletion of Akt1 promotes kidney fibrosis in a murine model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Biomed Res Int 2020; 2020: 6143542. |
| 30 |
Irazabal MV, Torres VE. Reactive oxygen species and redox signaling in chronic kidney disease. Cells 2020; 9: 1342.
DOI URL |
| 31 | Jin L, Luo ZY, Lu A. Piperlongumine induces apoptosis and pyroptosis of NCI-H460 lung cancer cells via increasing ROS. Zhong Guo Yao Xue Za Zhi 2020; 55: 1002-1007. |
| 32 | Abdelrahman RS, Abdelmageed ME. Renoprotective effect of celecoxib against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity through suppressing NFκB and caspase-3 signaling pathways in rats. Chem Biol Interact 2020; 315: 108863. |
| 33 |
Barrera-Chimal J, Pérez-Villalva R, Ortega JA, et al. Intra-renal transfection of heat shock protein 90 alpha or beta (Hsp90αor Hsp90β)protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014; 29: 301-12.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||