Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 530-538.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.04.003
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Drug response biomarkers of Pien Tze Huang (片仔癀) treatment for hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride
ZHANG Di1,2, WEI Muyun2, CHEN Luan2, WU Hao2, WANG Ting2, ZHANG Zhiruo2, ZHANG Ying2, YU Juan3, HUANG Jinming3, ZHU Jinhang1,2( ), QIN Shengying2(
), QIN Shengying2( )
)
- 1 School of Life Sciences, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, China
2 Bio-X Institutes, Key Laboratory for the Genetics of Developmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Ministry of Education, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200030, China
3 Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Pien Tze Huang Natural Medicine Research and Development, Zhangzhou Pien Tze Huang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Zhangzhou 350000, China
-
Received:2021-01-12Accepted:2021-03-22Online:2022-08-15Published:2022-07-12 -
Contact:ZHU Jinhang,QIN Shengying -
About author:Dr. ZHU Jinhang, Bio-X Institutes, Key Laboratory for the Genetics of Developmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Ministry of Education, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200000, China. zhujinhang@sjtu.edu.cn
Prof. QIN Shengying, Bio-X Institutes, Key Laboratory for the Genetics of Developmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Ministry of Education, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200000, China. chinsir@sjtu.edu.cn;
-
Supported by:the 863 program(2012AA02A515);the 863 program(2012AA021802);National Nature Science Foundation of China(81773818);National Nature Science Foundation of China(81273596);National Nature Science Foundation of China(30900799);National Nature Science Foundation of China(81671326);National Key Research and Development Program(2017YFC0909303);National Key Research and Development Program(2016YFC0905000);National Key Research and Development Program(2016YFC0905002);National Key Research and Development Program(2016YFC1200200);National Key Research and Development Program(2016YFC0906400);4th Three-year Action Plan for Public Health of Shanghai(Project 15GWZK0101);Shanghai Pujiang Program(17PJD020);Shanghai Key Laboratory of Psychotic Disorders(13dz2260500);Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province(2016J05210);the Anhui Medical University for Scientific Research of BSKY(XJ201607);Anhui Medical University for Scientific Research(2017xkj006)
Cite this article
ZHANG Di, WEI Muyun, CHEN Luan, WU Hao, WANG Ting, ZHANG Zhiruo, ZHANG Ying, YU Juan, HUANG Jinming, ZHU Jinhang, QIN Shengying. Drug response biomarkers of Pien Tze Huang (片仔癀) treatment for hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 530-538.
share this article
| Primer name | Sequence (5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| SP4-F | TTGCAGCAAGGCCAGCAGACC |
| SP4-R | GCTTCTTCTTTCCTGGTTCACTGCT |
| Fgf9-F | GCAGTCACGGACTTGGATCA |
| Fgf9-R | AATTCCAGAATGCCGAAGCG |
| Slc2a6-F | GCGACTCCTGGAGAGAGAGA |
| Slc2a6-R | CAGGATGCCTGGATTTTGTC |
| Hmga2-F | GCCAAGAGGCAGACCTAGGAAA |
| Hmga2-R | CATGGCAATACAGAATAAGTGGTCA |
| Tln2-F | CTGAGGCTCTTTTCACAGCA |
| Tln2-R | CTCATCTCATCTGCCAAGCA |
| Ank3-F | TCCAACCTCTCTGGGCCTTG |
| Ank3-R | CCCATGTTAGGTGAGTGCTCC |
| Pax9-F | ACCACATTTACTCATATCCCAGTCCCA |
| Pax9-R | GGCTCCCTTCTCCAATCCATTCA |
Table 1 Primer sequence of target genes
| Primer name | Sequence (5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| SP4-F | TTGCAGCAAGGCCAGCAGACC |
| SP4-R | GCTTCTTCTTTCCTGGTTCACTGCT |
| Fgf9-F | GCAGTCACGGACTTGGATCA |
| Fgf9-R | AATTCCAGAATGCCGAAGCG |
| Slc2a6-F | GCGACTCCTGGAGAGAGAGA |
| Slc2a6-R | CAGGATGCCTGGATTTTGTC |
| Hmga2-F | GCCAAGAGGCAGACCTAGGAAA |
| Hmga2-R | CATGGCAATACAGAATAAGTGGTCA |
| Tln2-F | CTGAGGCTCTTTTCACAGCA |
| Tln2-R | CTCATCTCATCTGCCAAGCA |
| Ank3-F | TCCAACCTCTCTGGGCCTTG |
| Ank3-R | CCCATGTTAGGTGAGTGCTCC |
| Pax9-F | ACCACATTTACTCATATCCCAGTCCCA |
| Pax9-R | GGCTCCCTTCTCCAATCCATTCA |

Figure 1 Expression level changes of α-SMA from second to eighth week (×400) The red staining sections represent the expression of α-SMA, and the blue staining parts represent the cell nuclear. A: the staining results of the Control group second week α-SMA; B: the staining results of the control group forth week α-SMA; C: the staining results of the Control group sixth week α-SMA; D: the staining results of the Control group eighth week α-SMA; E: the staining results of the PZH group second week α-SMA; F: the staining results of the PZH group forth week α-SMA; G: the staining results of the PZH group sixth week α-SMA; H: the staining results of the PZH group eighth week α-SMA. α-SMA: alpha-smooth muscle actin; PZH: Pien Tze Huang.
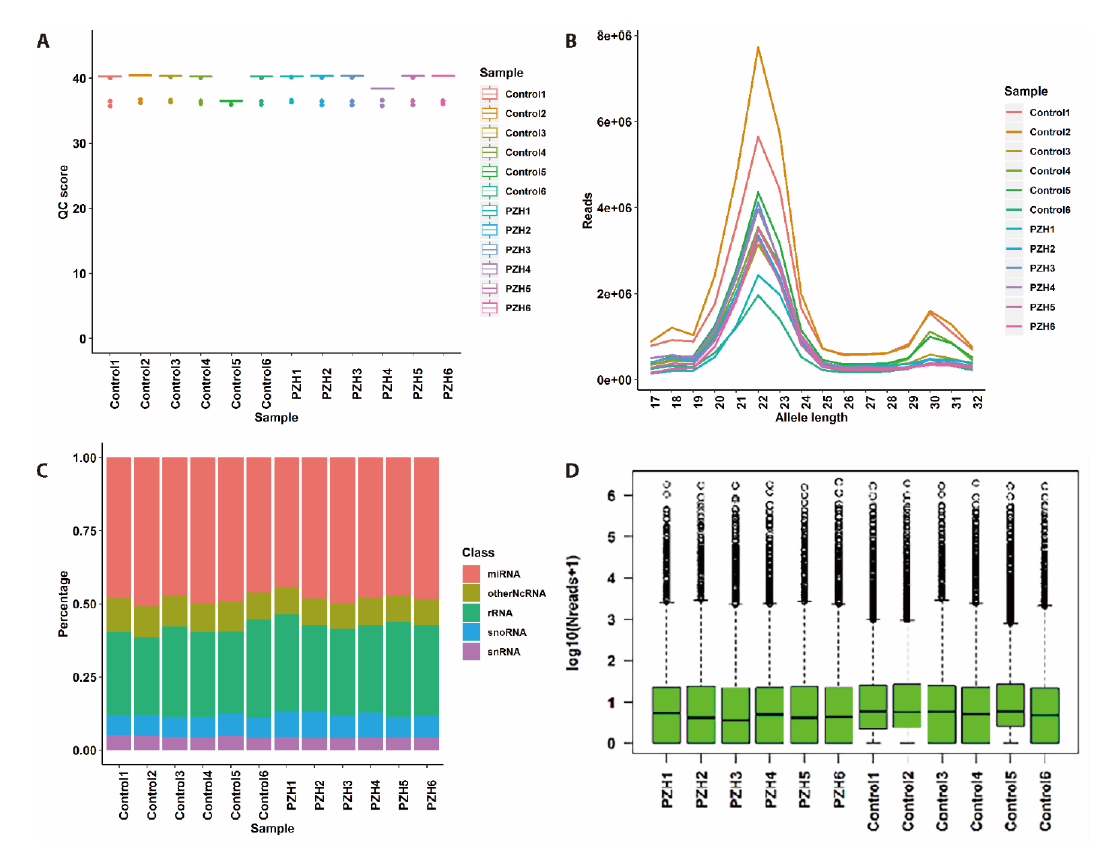
Figure 2 Results of sequenced data from quality control to miRNA expression A: the quality control score of all samples. The x axis represents sample name and the y axis represents quality control score; B: the miRNA reads and distributions of all samples in different lengths. The x axis represents miRNA length, and the y axis represents reads; C: the percentage of different small RNA accounted for total small RNA in each sample. The x axis indicates sample name and the y axis shows percentage accounted for total small RNA; D: the expression level of overall miRNA in each sample. The x axis is sample name and the y axis is expression level transformation. QC score: quality control score.

Figure 3 Analysis results of samples and differential expression miRNAs A: the clustering graph for total miRNA. The red color represents the high expression and the blue color represents the low expression; B: the clustering plot of top 20 differentially expressed miRNAs; C: the up-regulation and down-regulation miRNA. The x axis is log2 fold change and the y axis is the adjusted P value. The blue dots represent down-regulated miRNA; the red dots represent the up-regulated miRNA; the gray dots represent non-significant miRNAs. log2 (FC): log2 (fold change), -log10 (padj): -log10 (adjusted P value).
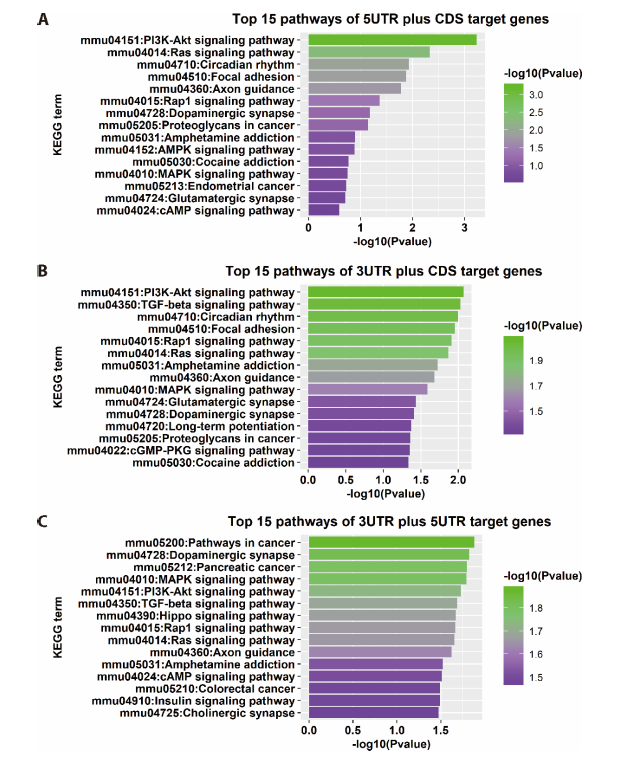
Figure 4 Analysis results of KEGG enrichment A-C: the 15 mostly enriched KEGG pathways identified by 3 different methods. The x axis is P value for enrichment corresponding pathway and the y axis is the pathway name. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
| Relative miRNA | MiRNA expression level | Target gene | Predicting gene expression | Related pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmu-miR-3064-5p | down | Slc2a6 | up | - |
| mmu-miR-205-5p | up | Tln2, Sp4 | down | Rap1 signaling pathway |
| mmu-miR-370-3p | up | Hmga2, Ank3 | down | Transcriptional misregulation in cancer |
| mmu-miR-205-5p | up | Pax9 | down | - |
| mmu-miR-665-3p | up | Fgf9, Pax9 | down | Rap1, Ras, MAPK, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway |
Table 2 Important miRNAs, their pathways and prediction expression level related with target genes
| Relative miRNA | MiRNA expression level | Target gene | Predicting gene expression | Related pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmu-miR-3064-5p | down | Slc2a6 | up | - |
| mmu-miR-205-5p | up | Tln2, Sp4 | down | Rap1 signaling pathway |
| mmu-miR-370-3p | up | Hmga2, Ank3 | down | Transcriptional misregulation in cancer |
| mmu-miR-205-5p | up | Pax9 | down | - |
| mmu-miR-665-3p | up | Fgf9, Pax9 | down | Rap1, Ras, MAPK, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway |
| 1 |
Friedman SL. Hepatic fibrosis: emerging therapies. Dig Dis 2015; 33: 504-7.
DOI PMID |
| 2 | Toosi AE. Liver Fibrosis: causes and methods of assessment, a review. Rom J Intern Med 2015; 53: 304-14. |
| 3 |
Xu F, Liu C, Zhou D, Zhang L. TGF-β/SMAD pathway and its regulation in hepatic fibrosis. J Histochem Cytochem 2016; 64: 157-67.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
Kong LJ, Li H, Du YJ, et al. Vatalanib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, decreases hepatic fibrosis and sinusoidal capillarization in CCl4-induced fibrotic mice. Mol Med Rep 2017; 15; 2604-10.
DOI URL |
| 5 |
Poilil Surendran S, George Thomas R, Moon MJ, Jeong YY. Nanoparticles for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Int J Nanomedicine 2017; 12: 6997-7006.
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Altamirano-Barrera A, Barranco-Fragoso B, Mendez-Sanchez N. Management strategies for liver fibrosis. Ann Hepatol 2017; 16: 48-56.
DOI PMID |
| 7 | Kagan P, Sultan M, Tachlytski I, Safran M, Ben-Ari Z. Both MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways are necessary for IL-6-dependent hepatic stellate cells activation. PLoS One 2017; 12: e0176173. |
| 8 |
Wu L, Zhang Q, Mo W, et al. Quercetin prevents hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and reducing autophagy via the TGF-beta1/Smads and PI3K/Akt pathways. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 9289.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Ying HZ, Chen Q, Zhang WY, et al. PDGF signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis and therapeutics (Review). Mol Med Rep 2017; 16: 7879-89.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Huang Y, Fan X, Tao R, et al. Effect of miR-182 on hepatic fibrosis induced by Schistosomiasis japonica by targeting FOXO 1 through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 2018; 233: 6693-704.
DOI PMID |
| 11 |
Jung YK, Yim HJ. Reversal of liver cirrhosis: current evidence and expectations. Korean J Intern Med 2017; 32: 213-28.
DOI URL |
| 12 |
Li SX, Mu Y, Zheng FY. Influence of gastrointestinal digestion and edible plant combination on oral bioavailability of triterpene saponins, using a biomimetic digestion and absorption system and determination by HPLC. J Agric Food Chem 2013; 61: 10599-603.
DOI URL |
| 13 | Qiu X, Luo H, Liu X, et al. Therapeutic potential of Pien Tze Huang on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis rat. J Immunol Res 2018; 2018: 2952471. |
| 14 | Qi F, Zhou S, Li L, et al. Pien Tze Huang inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by upregulating miR-16 expression. Oncol Lett 2017; 14: 8132-37. |
| 15 |
Zhao J, Hu H, Wan Y, Zhang Y, Zheng L, Hong Z. Pien Tze Huang Gan Bao ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury, oxidative stress and inflammation in rats. Exp Ther Med 2017; 13: 1820-26.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Lee KK, Kwong WH, Chau FT, Yew DT, Chan WY. Pien Tze Huang protects the liver against carbon tetrachloride-induced damage. Pharmacol Toxicol 2002; 91: 185-92.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Yang Y, Chen Z, Deng L, et al. Pien Tze Huang ameliorates liver injury by inhibiting the PERK/eIF2alpha signaling pathway in alcohol and high-fat diet rats. Acta Histochem 2018; 120: 578-85.
DOI PMID |
| 18 |
Xin X, Zhang Y, Liu X, Xin H, Cao Y, Geng M. MicroRNA in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2014; 19: 1418-24.
DOI URL |
| 19 |
Wang L, Zhu W, Dong Z, Song F, Dong J, Fu J. Comparative microRNA-seq analysis depicts candidate miRNAs involved in skin color differentiation in red tilapia. Int J Mol Sci 2018; 19: 1209.
DOI URL |
| 20 |
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2017; 16: 203-22.
DOI PMID |
| 21 | Vishnoi A, Rani S. MiRNA biogenesis and regulation of diseases: an overview methods. Mol Biol 2017; 1509: 1-10. |
| 22 | Zealy RW, Wrenn SP, Davila S, Min KW, Yoon JH. microRNA-binding proteins: specificity and function. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2017; 8: 10.1002/wrna.1414.10.1002/wrna.1414 |
| 23 |
Dong Z, Li S, Wang X, et al. lncRNA GAS5 restrains CCl(4)-induced hepatic fibrosis by targeting miR-23a through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2019; 316: G539-50.
DOI URL |
| 24 | Roy S, Benz F, Luedde T, Roderburg C. The role of miRNAs in the regulation of inflammatory processes during hepatofibrogenesis. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 2015; 4: 24-33. |
| 25 |
Jiang XP, Ai WB, Wan LY, Zhang YQ, Wu JF. The roles of microRNA families in hepatic fibrosis. Cell Biosci 2017; 7: 34.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U, Segal E. The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1278-84.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 2009; 19: 92-105.
DOI PMID |
| 28 |
Loher P, Rigoutsos I. Interactive exploration of RNA22 microRNA target predictions. Bioinformatics 2012; 28: 3322-3.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Lin JM, Wei LH, Chen YQ, et al. Pien Tze Huang induced apoptosis in human colon cancer HT-29 cells is associated with regulation of the Bcl-2 family and activation of caspase 3. Chin J Integr Med 2011; 17: 685-90.
DOI URL |
| 30 | Kitano M, Bloomston PM. Hepatic stellate cells and microRNAs in pathogenesis of liver. Fibrosis J Clin Med 2016; 5: 38. |
| 31 |
He X, Sun Y, Lei N, et al. MicroRNA-351 promotes schistosomiasis-induced hepatic fibrosis by targeting the vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018; 115: 180-5.
DOI URL |
| 32 | Schumacher JD, Guo GL. Regulation of hepatic stellate cells and fibrogenesis by fibroblast growth factors. Biomed Res Int 2016; 2016: 8323747. |
| 33 |
McDaniel K, Huang L, Sato K, et al. The let-7/Lin28 axis regulates activation of hepatic stellate cells in alcoholic liver injury. J Biol Chem 2017; 292: 11336-47.
DOI PMID |
| 34 |
Antoine M, Wirz W, Tag CG, et al. Expression and function of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 9 in hepatic stellate cells and its role in toxic liver injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 361: 335-41.
DOI URL |
| 35 | Cui H, Song R, Wu J, Wang W, Chen X, Yin J. MicroRNA-337 regulates the PI3K/AKT and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting high-mobility group AT-hook 2. Am J Cancer Res 2018; 8: 405-21. |
| 36 |
Xiao Y, Liu R, Li X, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 contributes to cholangiocyte proliferation and cholestatic liver fibrosis in biliary atresia. Hepatology 2019; 70: 1658-73.
DOI URL |
| 37 |
Yang YZ, Zhao XJ, Xu HJ, et al. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate ameliorates high fructose-induced liver fibrosis in rat by increasing miR-375-3p to suppress JAK2/STAT3 pathway and TGF-β1/Smad signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2019; 40: 879-94.
DOI PMID |
| 38 |
Li J, Xue J, Wang D, et al. Regulation of gasdermin D by miR-379-5p is involved in arsenite-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells and in fibrosis via secretion of IL-1β from human hepatic cells. Metallomics 2019; 11: 483-95.
DOI URL |
| 39 |
Lu CH, Hou QR, Deng LF, et al. MicroRNA-370 attenuates hepatic fibrogenesis by targeting smoothened. Dig Dis Sci 2015; 60: 2038-48.
DOI URL |
| 40 |
Wang P, Lei S, Wang X, et al. MicroRNA-134 deactivates hepatic stellate cells by targeting TGF-β activated kinase 1-binding protein 1. Biochem Cell Biol 2019; 97: 505-12.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHANG Junli, HE Ying, ZHANG Xia, FU Hongfang, HU Xiaoyu. Fuzheng Huayu preparation (扶正化瘀胶囊/片) combined with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate on hepatitis B: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 221-230. |
| [2] | WEI Lexin, LI Weiyi, TIAN Ting, ZHANG Ning, YANG Shijing, YANG Dongqing, LI Guochun, YE Fang. Identification of novel biomarkers and therapeutic target candidates for stasis-heat symptom pattern of acute intracerebral hemorrhage by quantitative plasma proteomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 622-632. |
| [3] | ZHANG Jiri Mutu, LIANG Shilong, NIE Peng, LIAO Yong’an, AI Qinying, YAN Xiaojun, LIU Hongning, JI Yanhua, ZENG Zhijun. Efficacy of Kushen decoction (苦参汤) on high-fat-diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 364-371. |
| [4] | Lei LIU, Hanbin GUO, Cuiping SHAO, Lin WANG, Youqing XU, Yiming ZHOU. Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang (疏肝活血化瘀方) attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 65-72. |
| [5] | Zhan Kai, Xu Yan, Han Mengling, Cheng Liangbin. Daifan San intervenes in forkhead box P3 and the interleukin(IL)-23/IL-17A signaling pathway to help prevent and treat primary biliary cirrhosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 571-583. |
| [6] | Zeng Chuang, Bai Xuejing, Qin Heping, Wang Hong, Rong Xiaofeng, Yan Jin. Effect of adjuvant therapy with electroacupuncture on bone turnover markers and interleukin 17 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(04): 582-586. |
| [7] | Gong Zhenghua, Deng Chaowen, Xiang Tianxin, Tao Lili, Xiao Hongbo, Peng Yanzhong, Zheng Jie, Hu Guoxin. Effect of Dahuang Zhechong pills on long non-coding RNA growth arrest specific 5 in rat models of hepatic fibrosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(02): 190-196. |
| [8] | FO Balogun, AOT Ashafa. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of Dicoma anomala Sond.aqueous root extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in Wistar rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(04): 504-513. |
| [9] | Yang Lihua, Wang Yun, Wang Xiaohua, Liu Yanqing. Effect of allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of hepatic cirrhosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(01): 63-68. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||